Bacteria develop tougher membranes to resist antibiotics, report into superbugs finds

Scientists have identified how deadly bacteria resist antibiotics at a molecular level for the first time, in a discovery that could have significant implications for the development of much-needed new drugs.
According to a report published in Nature Scientific Communications this week, bacteria develop stronger cell membranes as they become resistant, repelling antibiotics and preventing effective treatment.
The discovery could help design much-needed new antibiotics to fight growing drug-resistance – which the World Health Organization has listed as one of its top threats to global health.
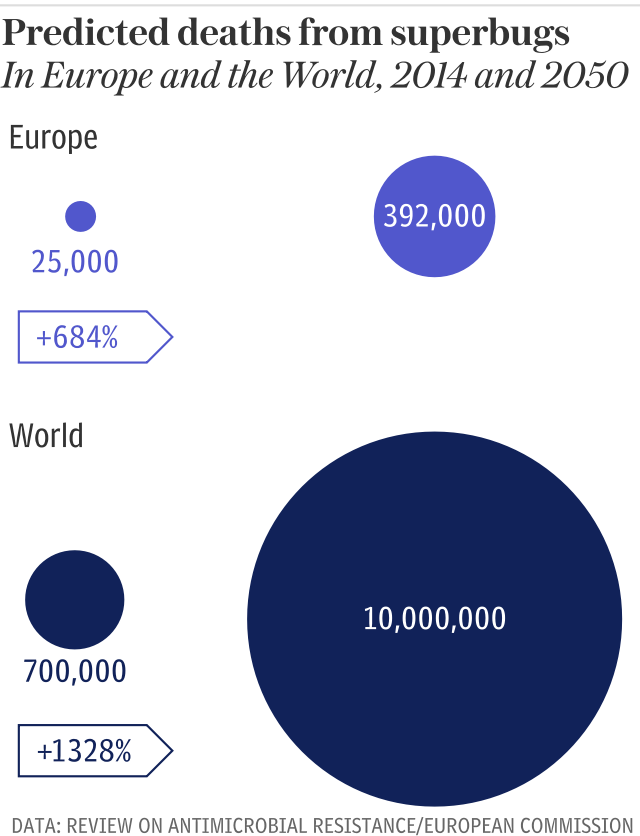
Current estimates suggest that nearly 10 million people a year will die from untreatable superbugs by 2050, a dramatic increase from the 700,000 deaths linked to antibiotic resistance in 2014.
In the new study, researchers looked at how 10 different bacteria developed resistance to the drug polymyxin B (PmB), which is commonly used to treat meningitis and urinary tract infections.
Up until 2016 the antibiotic was considered to be one of the most effective drugs of its kind, a last resort when all others failed.
The team found that all the bacteria developed tougher membranes as they became more resistant, which prevented the antibiotics penetrating into the centre of the molecule and killing the cell.
“The bacterial membrane becomes tougher and more resistant against penetration,” said Maikel Rheinstädter, a professor of biophysics at McMaster University in Canada and lead author of the study. “This makes it harder for the antibiotics to poke through and effectively stab the bacteria.”
The cells also lessened their negative charge, reducing the attraction to the positively charged antibiotics and again making it more difficult for the drugs to target the bacteria.

“In the past, individual diseases and bacteria have all been treated differently,” said Professor Rheinstädter. “So it is important that we have established that these bacteria all have common properties, as it makes tackling resistance easier.”
The physicists used a powerful microscope, worth around $1 million (£765,000), to view the tiny bacterial molecules, which are roughly a million times smaller than a strand of hair.
They believe the model will inform the development of future antibiotics, as well as help scientists understand why drugs currently available have become ineffective.
“We will continue to look at different antibiotics and offer our toolkit to others, to screen antibiotic candidates or explain why antibiotics no longer work,” said Professor Rheinstädter.

Protect yourself and your family by learning more about Global Health Security

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
