Ban plug-in hybrids: cars will account for 10 per cent of UK's carbon emissions by 2035

Plug-in hybrid cars will be responsible for 10 per cent of Britain's carbon emissions by 2035, according to analysis conducted for The Telegraph, amid rising concern they are being wrongly touted as a green option for drivers.
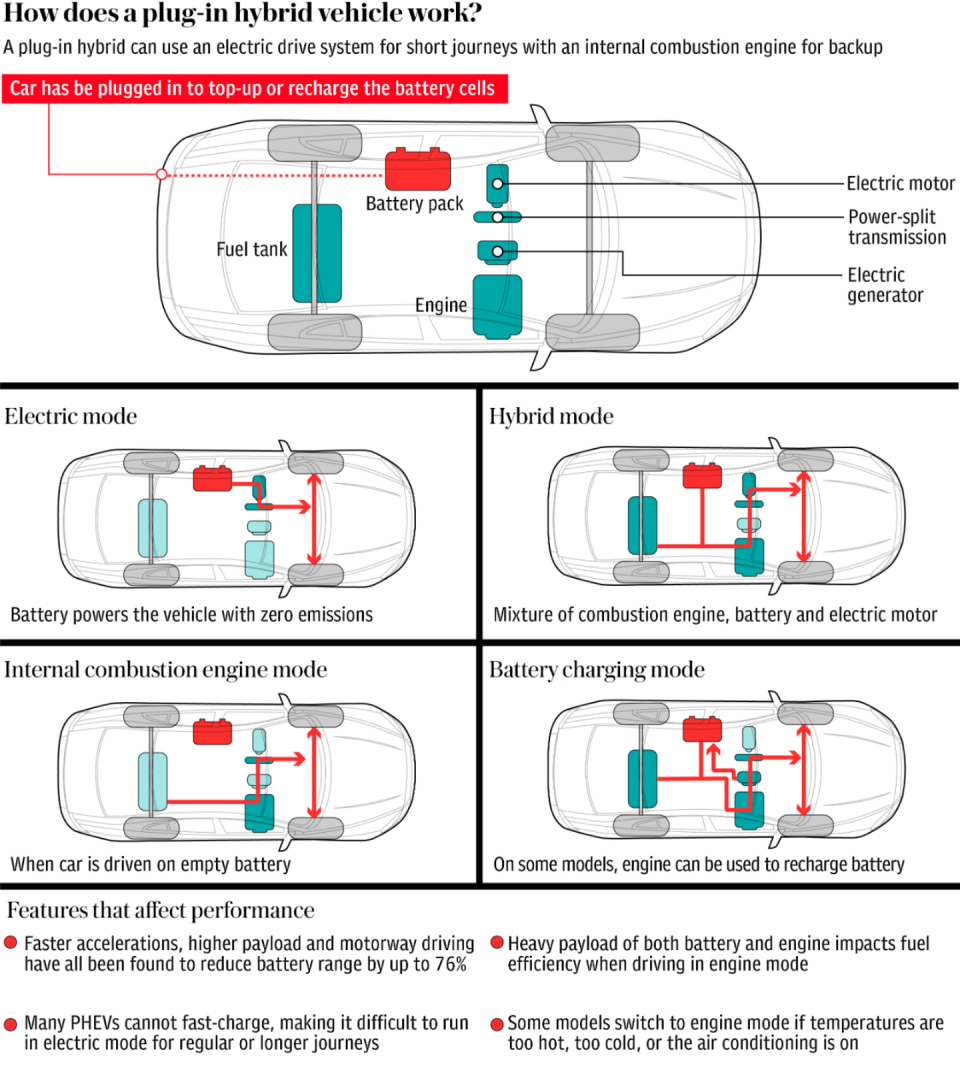
The Government has said hybrid cars, which use both battery and internal combustion engine technology, will continue to be sold for five years beyond the 2030 deadline for the phase-out of new petrol and diesel cars.
But analysts say this will damage the country’s efforts to get to net zero Co2 emissions because PHEVs have been shown to emit up to four times as much in real-world scenarios than in official tests.
Sales of PHEVs are expected to double in 2021, and grow to as much as 50 per cent of the market by the 2030s unless the Government imposes stringent criteria on sales, potentially posing a problem for the UK’s emissions targets.
Analysis from NGO Transport and Environment for The Telegraph suggests that by 2035 emissions from 6.6 million PHEVs on the road could be as much as 20 million tonnes of Co2, around 10 per cent of all annual emissions as projected by the Government’s climate change advisers, the Climate Change Committee (CCC).
By 2050, when the UK should be at net zero emissions, it calculates that PHEVs could contribute between 1.4 and 5.9MtCo2.
Greg Archer, the NGO’s UK director, said the Government could limit the number of the most polluting vehicles on the road with strict criteria for post-2030 sales, which it suggests could cut emissions by around 75 per cent.
Analysis by the CCC shared with The Telegraph suggests that extending sales until 2035 could lead to an extra five million PHEVs on the road, which will more than double the contribution of hybrids to road transport emissions by 2050.
The majority of these sales will replace zero-emission battery cars, the CCC said, and contribute 35MtCo2 between 2035 and 2050,
The Government will begin a consultation in the next few weeks on which hybrids can be sold, and the CCC has called for stringent conditions to be applied.
Eoin Devane, senior transport analyst at the CCC, said the Government must “ensure that hybrids play a declining role relative to pure electric vehicles, and a minimal role beyond 2030, to avoid risking higher emissions”.
Campaigners say drivers risk being misled by green claims around plug-in hybrid cars.
It emerged last week that the Society of Motoring Manufacturers lobbied for the 2035 delay ahead of the ban, writing in a briefing paper for the Government that “the important role that PHEVs can play in reducing Co2, both now and in the future, must not be forgotten”. The briefing was revealed in a Freedom of Information Request by the New Scientist.
A study of around 100,000 PHEVs by the International Council on Clean Transportation, a US non-profit group, found that real-world driving emissions were two to four times higher than in official tests.
Another study, commissioned by the German government, found PHEVs emit up to three times more Co2 emissions than official tests claim, and could jeopardise Germany’s climate change targets.
Emerging data on real-world emissions from plug-in hybrids has been likened to the diesel emissions scandal, although there is no indication manufacturers have circumvented requirements of official tests.
Rather, official tests fail to consider real-world driving conditions, particularly frequency of recharging and distance travelled, but also the use of heating, which on some models can automatically switch the car to engine mode.
Mr Archer said: “There is a danger that once again, the car industry will be discredited by overclaiming on the environmental performance of cars and under delivering.”
Many car manufacturers have relied on the purported Co2 emissions from plug-in hybrids to meet stringent new targets across their fleet, as they try to offset the rising popularity of SUVs, which bring in greater profits.
Mr Devane said PHEVs could be a “useful transition technology” when charged appropriately.
But he added: “Evidence shows that in real-world use plug-in hybrids typically drive on petrol power up to two-thirds of the time, making their real-world emissions more comparable with conventional vehicles than with fully electric vehicles.”
Mike Hawes, the chief executive of the SMMT said: “We cannot comment on unverified, unregulated tests. Official figures used by manufacturers’ are produced from the internationally recognised WLTP test, a test undertaken in repeatable conditions, witnessed and certified by government authorities and the test data is required by law to be published with every vehicle.”
Mr Hawes added that official tests “consistently prove plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs) can deliver substantial emissions reductions compared to their pure petrol and diesel counterparts”. He said PHEVs were an important “stepping stone” for drivers who are not ready to switch to full EVs.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
