Captain of Britain’s new aircraft carrier says he 'would love an an extra 10,000 sailors’ to bring the Royal Navy up to strength

The captain of Britain’s new aircraft carrier has said he would like to see the Royal Navy recruit an extra 10,000 new sailors to bring the fleet up to strength.
With more than 32,000 personnel making up the full time strength of the Royal Navy and Royal Marines, Captain Jerry Kyd, the commander of aircraft carrier HMS Queen Elizabeth, the Royal Navy’s largest and most powerful warship, said retention and recruitment were a “constant battle” for senior officers.
Speaking after the Defence Secretary Gavin Williamson visited the carrier during its week-long visit to New York, Captain Kyd said it would be "lovely" to increase the size of the Royal Navy by 10,000 sailors over the coming years.
"This again is why we are looking at innovative manning," he said. "It is a constant battle - you have to have a strategy which balances your ends, ways and means.
"It would be lovely if we had another 10,000 people in the Navy... we are OK, we are balanced, we are getting back into balance.”
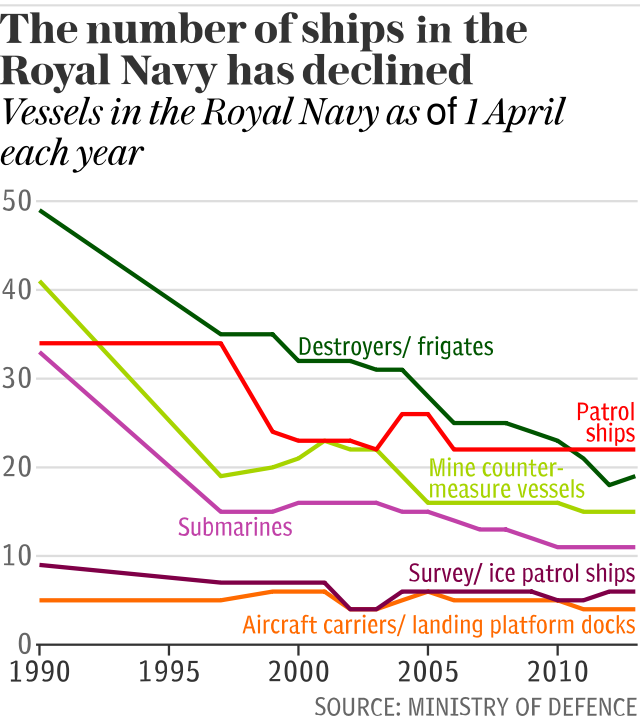
His comments, which come as he hands over command of HMS Queen Elizabeth on Wednesday, follow new figures from the Ministry of Defence which revealed that alack of sailors has meant four four British warships have not spent a day at sea in 2018.

Responding to a parliamentary question last week, the MoD released figuring showing a drop in activity for the Royal Navy’s fleet of Type 23 frigates due to ageing hulls and undermanning.
A National Audit Office report in April showed that the Royal Navy suffered a manpower shortage of 16 per cent in 2016/17.
Captain Kyd said the biggest challenge for the Royal Navy “is making sure there is balance across different branches” of the force, as it adds new vessels to the fleet and adapts to new challenges.
He said:"It is not numbers as such, it is the right quality of people in the right numbers in the right areas." He said retention rather than recruitment is more of an issue, and that they are constantly looking for ways to make it more attractive as a career."
Captain Kyd also revealed that the sister ship of HMS Queen Elizabeth, HMS Prince of Wales, is "on the gradual build up" with more than 500 personnel forming the ship's company so far.
With HMS Queen Elizabeth due to enter operational service in 2021, he said the combination of aircraft carriers, cutting-edge jets, Type 45 destroyers and astute class submarines will probably mean it is the "most potent a military task group we will have put together since 1982".
He added: "It is a strategic and political tool... it is all about deterrence."
Speaking on a visit to the ship on Saturday, Mr Williamson said the warship is a "clear sign and clear demonstration" of Britain's capability Britain.
"It is quite obvious to me that she is going to be an enormous asset to the Royal Navy, and really is an outward sign of rebirth of the Royal Navy, and actually a much more global Navy," he said.
"You can see so much of that happening already in the last year, with HMS Sutherland and HMS Albion playing an important role in the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
"This is the clearest demonstration that we are back in the league of being a great global navy that is able to project power, project influence and make a difference in every sea and ocean."
A shortage of sailor is particularly acute in the Royal Navy's surface fleet of frigates and destroyers.
First commissioned in 1989, the Type 23 Frigates have a planned 18-year lifespan which has been regularly extended. As they age the frigates need more time in maintenance as systems require updating or refitting.
The fleet is due to be replaced by eight Type 26 ships, the first of which is currently under construction in Scotland.
Increasing naval deployments from six to nine months due to the lack of sailors has meant that ships are alongside for greater periods before the tour, to allow service personnel time with their families.
In turn this means a longer maintenance period is required at the end. The ships are also in port for about two weeks in the middle of a deployment for crew leave.

Post-deployment each frigate will revert to a very low readiness state.
Each costing about £130 million, the Type 23 frigates are all named after British Dukes and are known as ‘Duke Class’. Based in Portsmouth and Devonport the primary role of the ships is anti-submarine warfare, through the use of a towed array sonar which trails behind the ship, electronically listening for emissions from submarines.
The data show that since 2010 the entire Type 23 fleet has spent a total of 32.5 years at sea. Assuming a crew of 185 sailors this equates to roughly 2.2 million man-days. On average that means each frigate has spent around 28.5 per cent of its time at sea annually. This figure will vary widely depending on the role of the vessel at the time and serviceability state.
However, 'days at sea' can be an unhelpful metric when assessing the value to the taxpayer. Many tasks require a serviceable ship to be in port. For example, the Fleet Ready Escort role requires a ship to be available for immediate tasking, such as for escorting Russian warships through the Channel.
Ships on deployment will also spend many days in port for maintenance, replenishment or to host visitors and foreign VIPs. Many UK defence sales come from such engagements.
Last week the Telegraph reported that a number of training exercises in UK waters now happen from Monday to Friday, allowing servicemen and women to go home at weekends and shortening the overall time ships spend at sea.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
