Chest X-rays miss nearly quarter of lung cancers, review finds
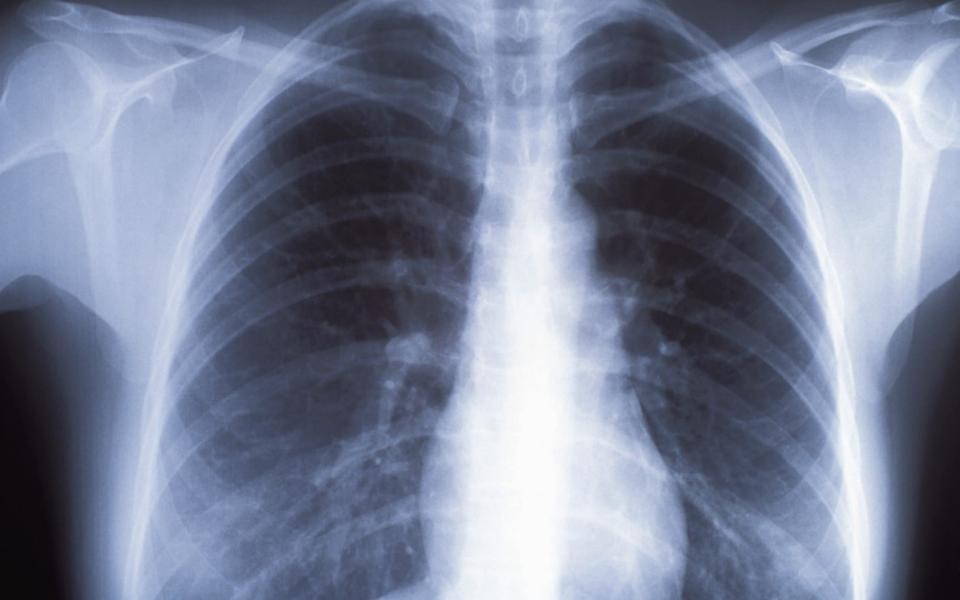
Lung Cancer is being missed at an early opportunity in almost a quarter of cases due to the use of out-dated X-rays, researchers have found.
A review in the British Journal of General Practice reveals that despite being the recommended method for investigating suspicious symptoms, such as persistent coughs or chest aches, X-rays miss up to 23 per cent of patients with the disease.
Its authors say this may partly explain the UK’s poor survival rates when compared to similar European countries.
Accounting for more than 35,000 deaths each year, lung cancer is the biggest cancer killer, with fewer than one in 10 patients surviving for five years after diagnosis.
Unlike many other cancers, rates have barely improved over the past 40 years.
Researchers at the universities of Leeds and Exeter drew on data from 21 previous studies involving more than 1,000 patients.
They concluded that the X-ray sensitivity for detecting lung cancer was between 77 and 80 per cent.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends GPs order an X-ray - which cost around £25 each - in the first instance if they suspect lung cancer.
However, the study authors suggest CT (computed tomography) scanning, which costs significantly more and is time-consuming, should be considered as a replacement first-line test.
They wrote: “X-ray has been with us for a long time but surprisingly, there has been very little research into how accurate it is for diagnosing lung cancer.”
The scientists added: “If chest X-ray were a novel technology, it is debatable whether the available evidence would be deemed sufficient to support its implementation as a diagnostic test for lung cancer.
“Our lung cancer outcomes still lag behind other high income countries, with less patients diagnosed at early stages of the illness.
“There are likely to be many reasons for this, but this research suggests that one factor could be our reliance on chest X-ray, compared to other countries that make more use of tests like computed tomography scans.”

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 