'Major breakthrough' as NHS rolls out £5 steroid that reduces deaths for most severe Covid-19 cases

A £5 steroid which is already available in NHS hospitals cuts deaths of people on ventilators by one third and will be rolled out within 24 hours.
Dexamethasone, an anti-inflammatory medication used to treat arthritis, severe allergies and asthma, is the first drug that has been shown to save lives and experts hailed the results as a ‘major breakthrough.’
A trial of 2,100 patients showed that it reduced the death rate of people on ventilators by 30 per cent. Currently four in 10 patients with the most severe form of Covid-19 who need mechanical ventilation will die.
The steroid saves one life for every eight patients on ventilators, meaning just two people instead of three will die. It also cuts the death rate of people needing oxygen by one fifth.
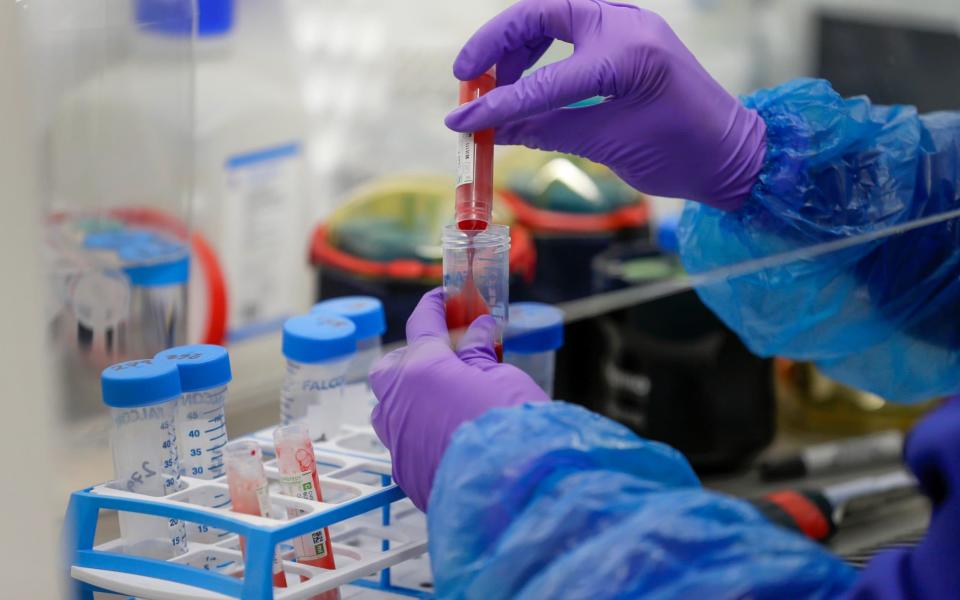
Scientists at Oxford University who have been carrying out the trials said up to 5,000 lives could have been saved if they had known about the drug at the beginning of the epidemic.
Martin Landray, Deputy Chief Investigator added: “It is a major breakthrough in a number of regards.
“Since the advent of this disease less than six months ago the search has been on for a treatment that actually reduces the risk of dying and there hasn’t been one until today. Now there is one.
“The results are sufficiently clear and people can be treated this evening. That’s a major major step forward.
“This is not an expensive drug, this is not a drug where there are supply chain issues or manufacturing issues, this is a drug that is globally available, so that is enormously important.
“It’s going to be hard for any drug to replace this given that for less than £50 you could take eight patients and save a life.”
The NHS has already given the go ahead for the treatment to be used in hospitals, and those on ventilators are likely to start receiving the steroid from Wednesday.
Professor Stephen Powis, NHS medical director added: “This is a huge breakthrough in our search for new ways to successfully treat patients with covid, both in the UK and across the world.
"It is thanks to NHS staff and patients who participated in the trial that from now, we are able to use this drug to dramatically improve Covid-19 survival for people in hospital who require oxygen or ventilation.”
NHS chief executive Simon Stevens added: "NHS hospitals, researchers and clinicians have worked together at breakneck speed to test new treatments for covid-19, and it is amazing to see work that would normally take years bear fruit in just a matter of months.
"This research agility is not only important for coronavirus patients, but augurs well for the streamlined innovation that the NHS and the UK life sciences now must pioneer."
The results are part of the Recovery (Randomised Evaluation of COVid-19 thERapY) trial, which was set up in March to test a range of potential treatments for COVID-19, including low-dose dexamethasone (a steroid treatment). More than 11,500 patients have been enrolled from over 175 NHS hospitals in the UK.
In the dexamethasone arm, patients were given a low dose of the steroid once a day for 10 days and compared to those who were given usual treatment without the extra medication.
Among the patients who received usual care alone, 28-day mortality was highest in those who required ventilation (41 per cent), intermediate in those patients who required oxygen only (25 per cent), and lowest among those who did not require any respiratory intervention (13 per cent).
Dexamethasone reduced deaths by one-third in ventilated patients and by one fifth in other patients receiving oxygen.
However there was no benefit among those patients who did not require respiratory support suggesting that the drug works once the immune system has gone into overdrive and inflammation has stopped the lungs being able to function properly.
The researchers said the drug should become the standard of care in the most sick patients.
Peter Horby, Professor of Emerging Infectious Diseases and Global Health in the Nuffield Department of Medicine and Chief Investigator of the RECOVERY trial said: “This is the only drug that has so far been shown to reduce mortality and it reduces it significantly. It is a major breakthrough.”
“The survival benefit is clear and large in those patients who are sick enough to require oxygen treatment, so dexamethasone should now become standard of care in these patients.
“We have spoken to the NHS and advice will be going out 24 hours. Those 400 patients still on ventilators should be placed on this drug unless there is a clear reason why not to.”
Government’s Chief Scientific Adviser, Sir Patrick Vallance, described the results as 'truly remarkable'.
“This is tremendous news today from the Recovery trial showing that dexamethasone is the first drug to reduce mortality from COVID-19. It is particularly exciting as this is an inexpensive widely available medicine.
“This is a ground-breaking development in our fight against the disease, and the speed at which researchers have progressed finding an effective treatment is truly remarkable. It shows the importance of doing high quality clinical trials and basing decisions on the results of those trials.”

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
