Nasa satellite Cassini set for grand finale with fiery plunge to destruction as it enters Saturn's orbit
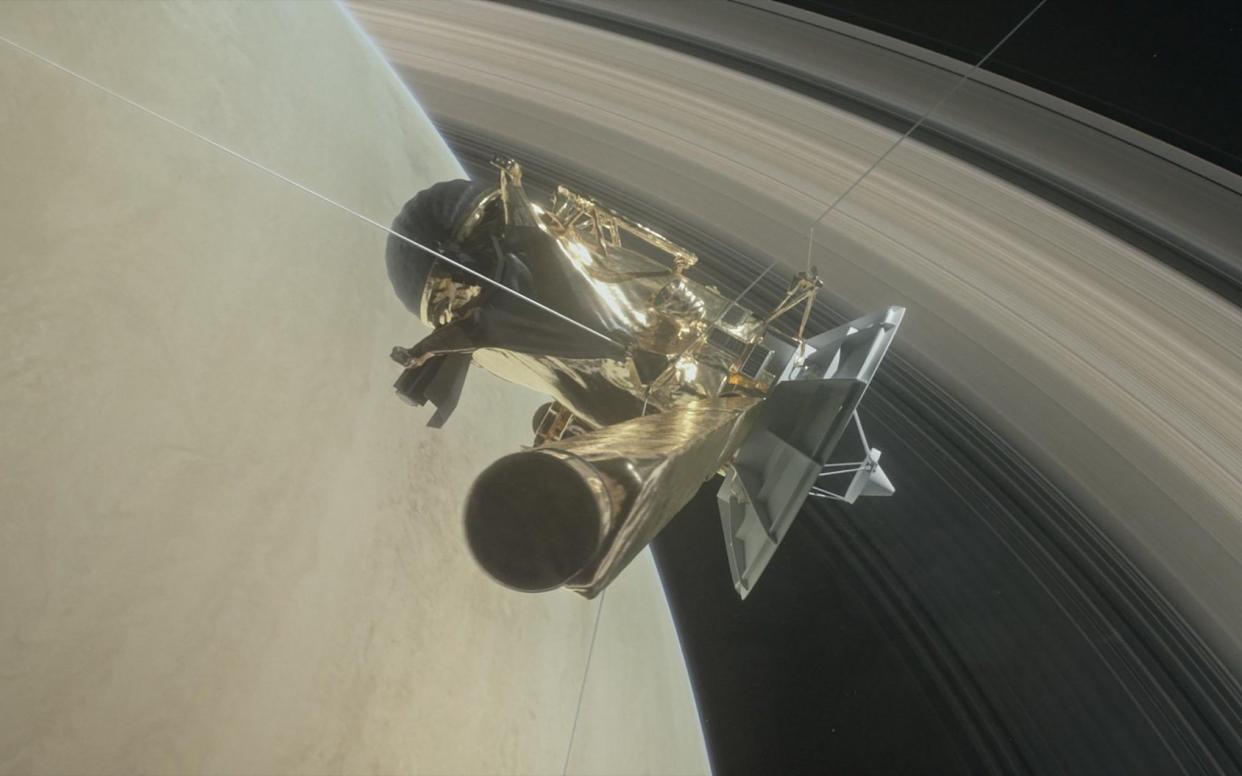

Nasa's Cassini spacecraft which launched 20 years ago to explore Saturn is set for a spectacular grand finale to its mission as it is sent into the planet's atmosphere where it faces certain destruction.
The manoeuvre brings an end to 12 years of exploration around the planet because the probe's propellant tanks used for adjusting its course are all but empty.
Cassini has been hunting for signs of life on Saturn's moon and recently discovered that all the conditions for it to thrive exist in the oceans of Enceladus.
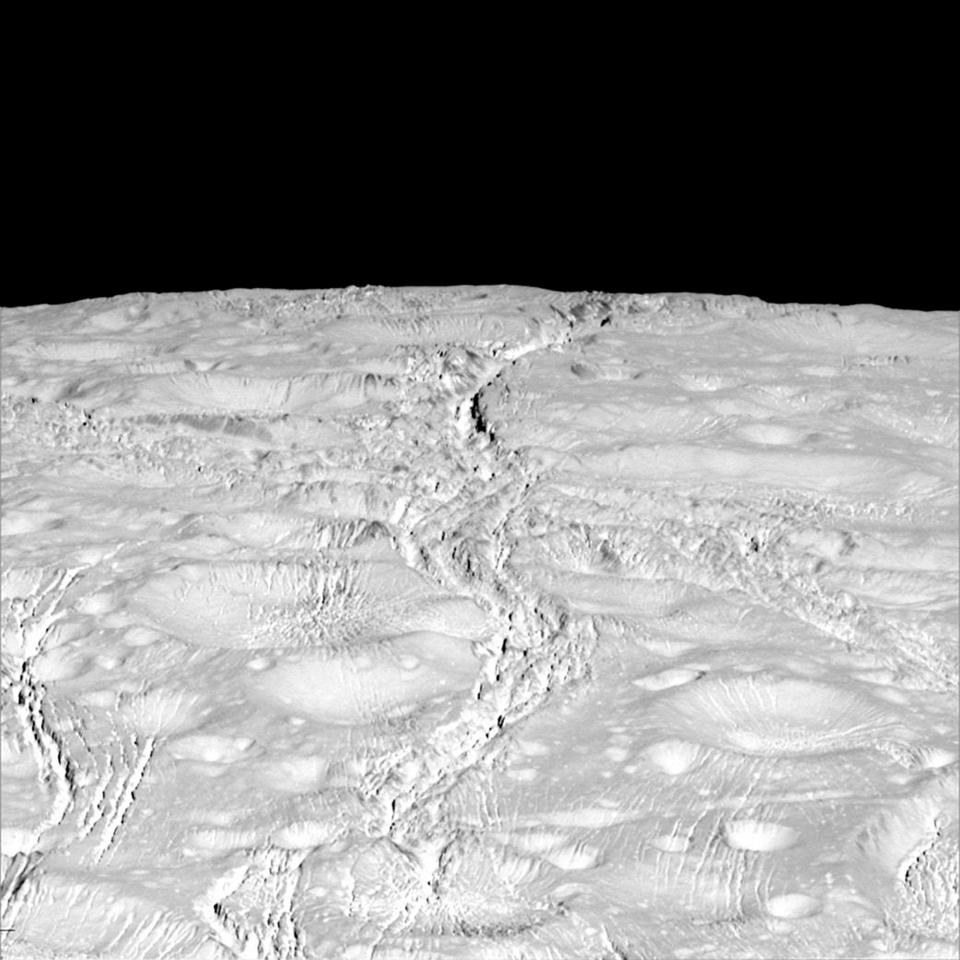

Nasa said the move will ensure its doesn't actually contaminate any of the moons around the planet, with the finale set for September 15.
However, keen not to waste the opportunity to study the secrets behind the captivating planet's unique appearance, it will continue to broadcast new photos and scientific readouts after beginning the dive on April 26.
Happening NOW: our final close flyby of #Saturn's moon #Titan, simulated here in @NASA_Eyes. Details: https://t.co/0QmYqS0KZRpic.twitter.com/PSf582lsjy
— CassiniSaturn (@CassiniSaturn) April 22, 2017
It will ultimately end in spectacular fashion as Cassini will break apart and melt, burning up like a meteor, and become part of the planet it left Earth to explore.
The satellite is controlled from the Earth with radio signals which take 68 to 84 minutes to reach the spacecraft.
Dr Earl Maize, Nasa's Cassini programme manager, told the BBC: "If Cassini runs out of fuel it would be uncontrolled and the possibility that it could crash-land on the moons of Titan and/or Enceladus are unacceptably high.
"We could put it into a very long orbit far from Saturn but the science return from that would be nowhere near as good as what we're about to do."
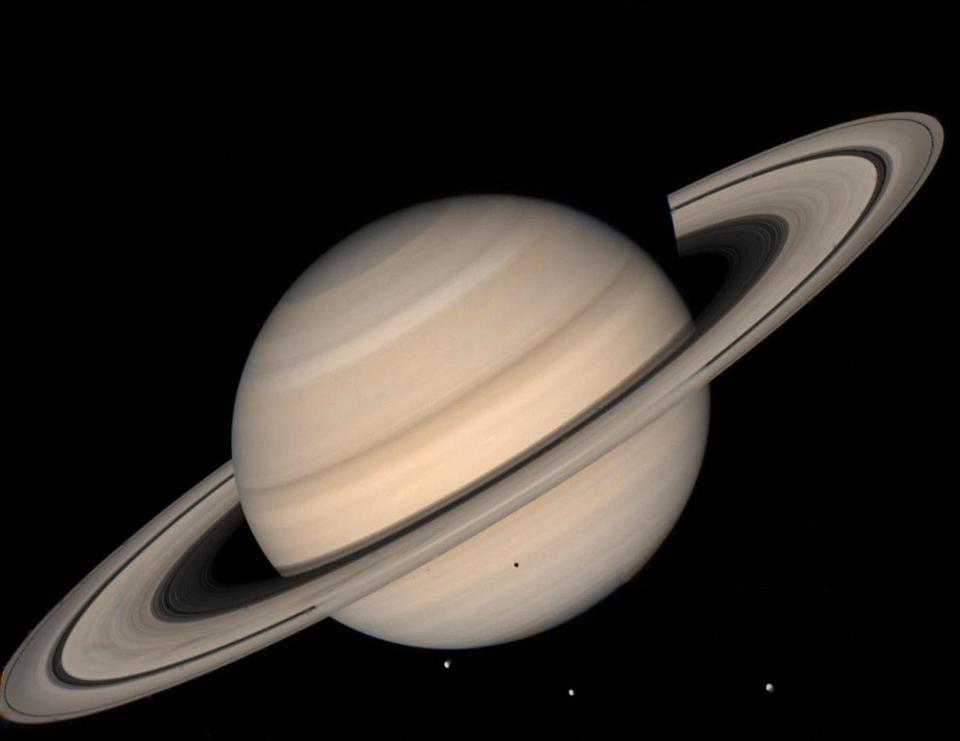
Such was the success of Cassini's discoveries that it inadvertently authored its own demise. Controllers don't want to risk the prospect of the satellite one day crashing into, and potentially damaging, the moons it has revealed capable of one day supporting life.
Instead, it made a final flyby of Saturn's biggest moon Titan – using its radar to reveal the surface lakes and seas one last time. Nasa hope to collect more data on Titan's "magic island", a feature in one of the moon's seas that changed in appearance over the course of several flybys.
On previous orbits of Titan, of which there have been 126, it has used the propellant to kick it into a new direction and explore other areas of the moon.
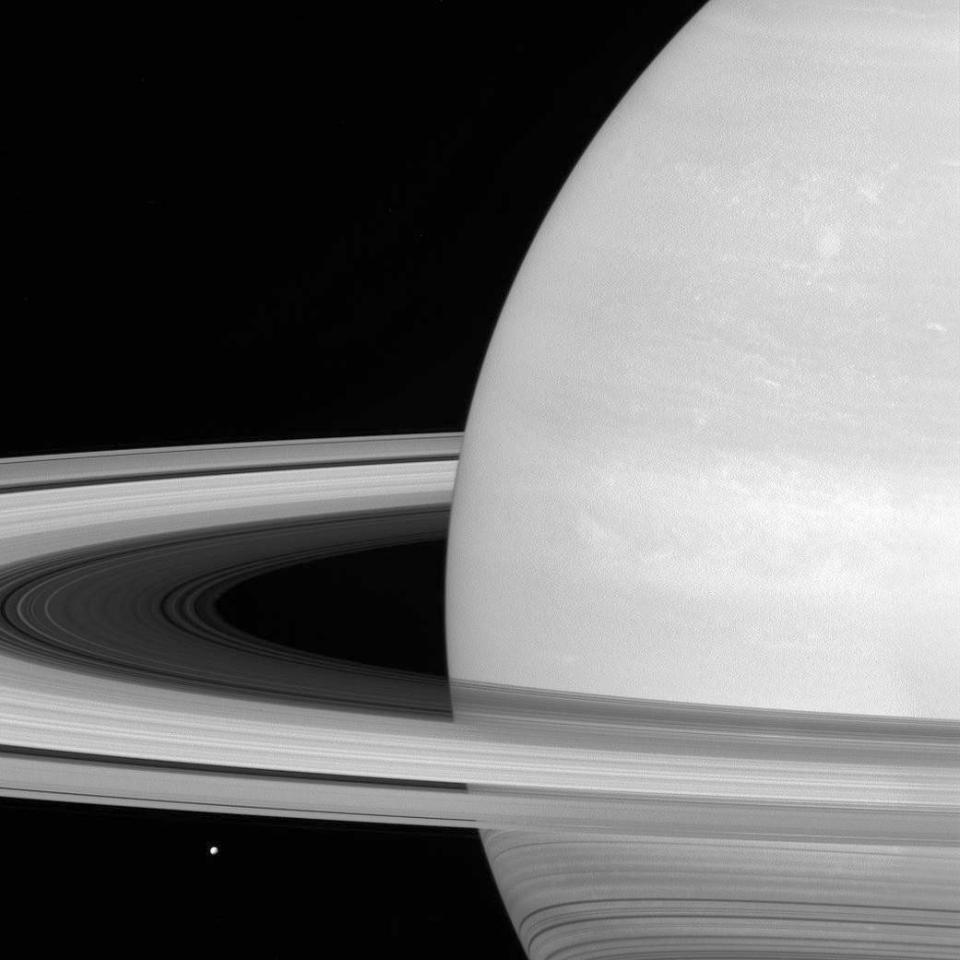
But following its final orbit, it will use the gravitational slingshot from Titan to sweep it into the path of the planet's orbit at around 13,000mph .
Prior to destruction, Cassini is set for 22 orbits between the planet and its rings before entering its atmosphere.
Just yesterday, it broadcast a picture of Earth seen from the outer edge of Saturn.
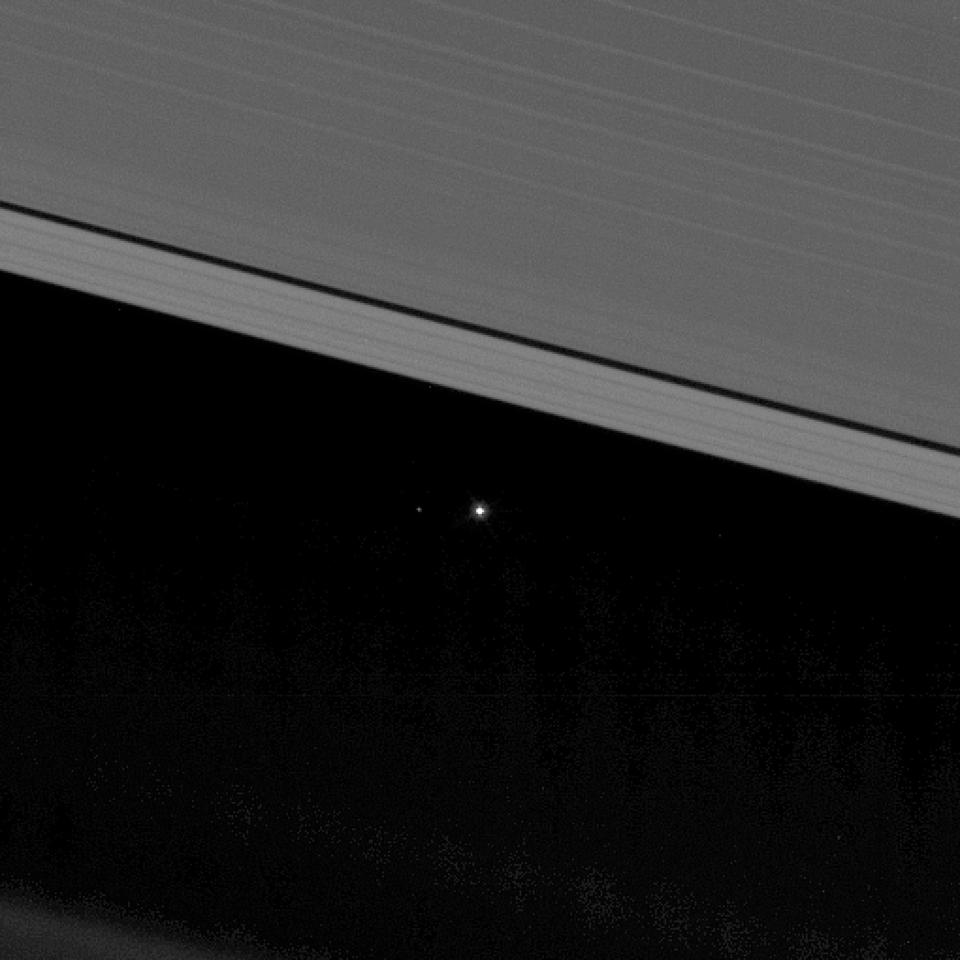

A Nasa spokesperson said: "While it's always sad when a mission comes to an end, Cassini's finale plunge is a truly spectacular end for one of the most scientifically rich voyages yet undertaken in our solar system.
"From its launch in 1997 to the unique grand finale science of 2017, the Cassini-Huygens mission has racked up a remarkable list of achievements."
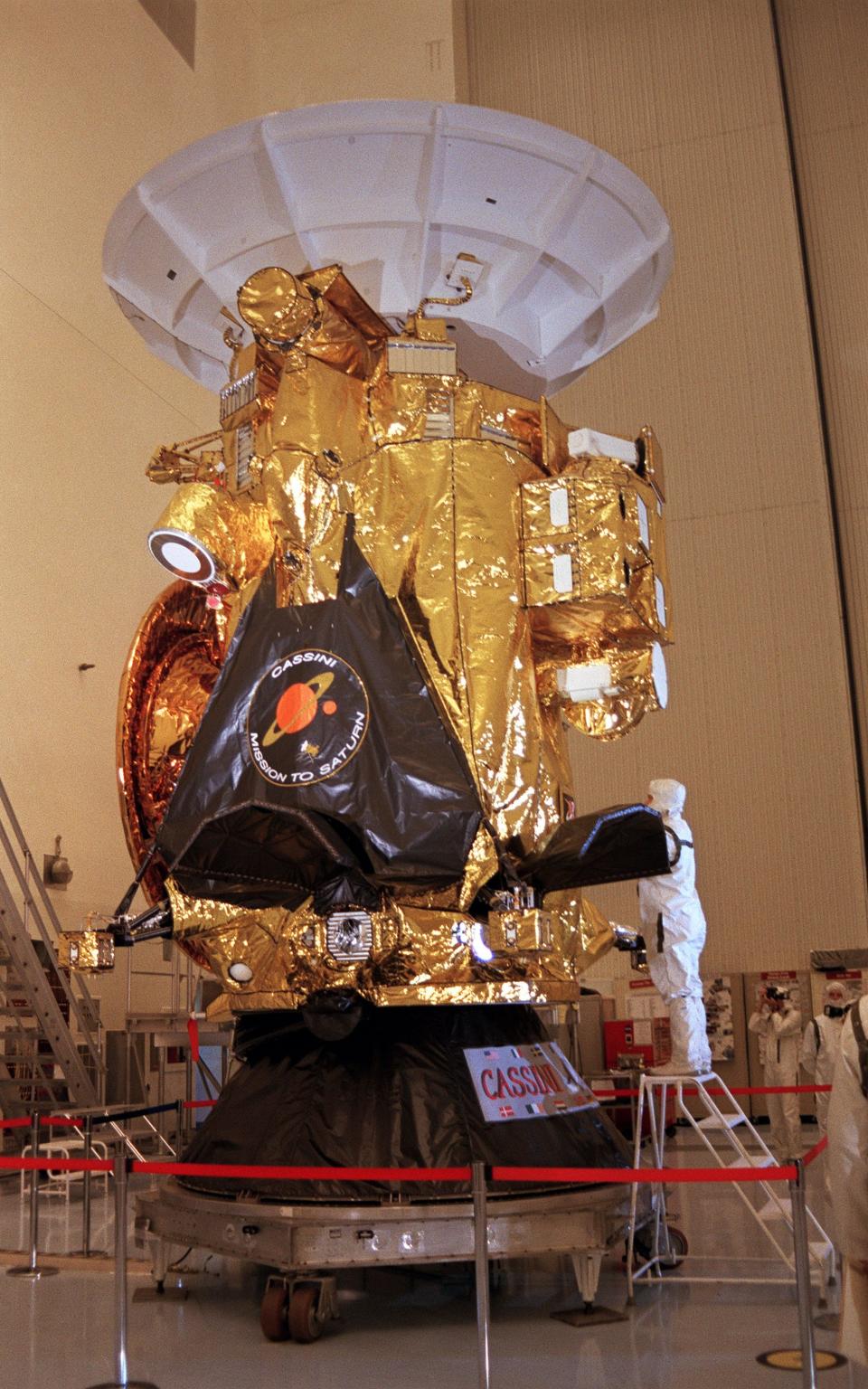
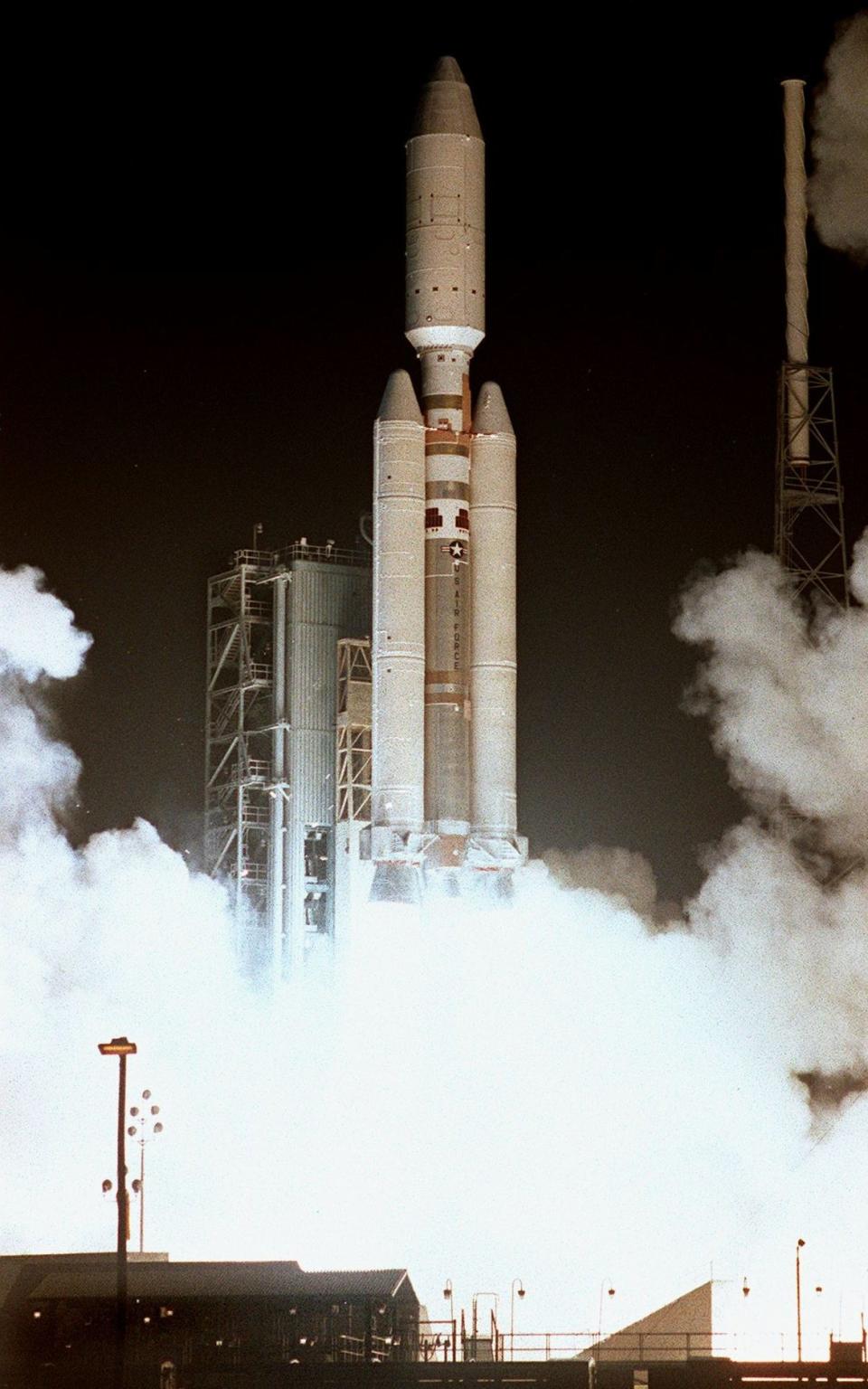


It took seven years for the probe to reach Saturn from Earth, twice passing by Venus before using the gravitational assist to propel it away from the sun and towards Saturn - passing by Earth and Jupiter on its way. The technique is used as a propellant saving initiative in space exploration.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
