Who is Nicola Sturgeon, leader of the SNP, and who can vote for them?

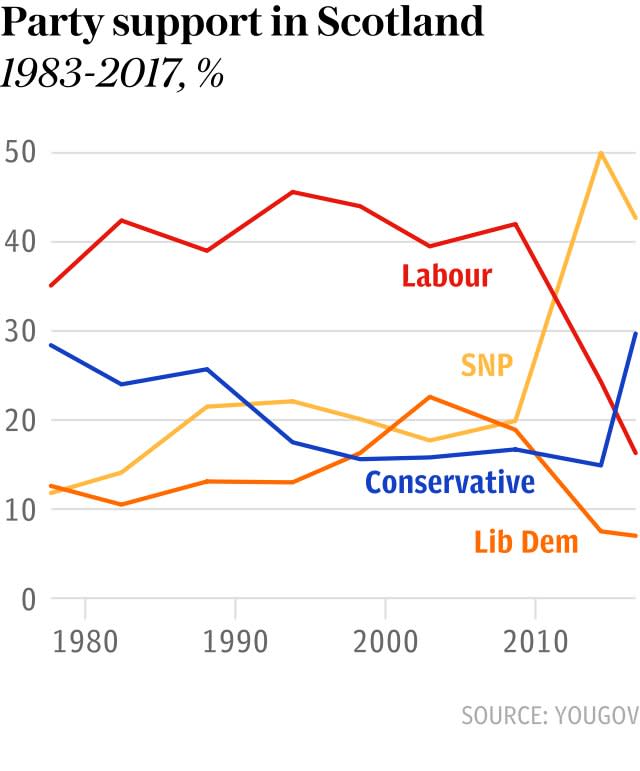
Former Scottish National Party leader Alex Salmond and deputy leader Angus Robertson have been dramatically ousted from Westminster as the SNP lost 21 seats across Scotland in the 2017 general election - putting plans for a second vote on independence in jeopardy.
After making stunning gains in 2015, Nicola Sturgeon's party lost seats to the Conservatives, Labour and the Liberal Democrats to see their numbers slashed to 35 MPs.
Here's everything you need to know Ms Sturgeon, her party, and her campaign for independence.
Who is Nicola Sturgeon?
The First Minister of Scotland and leader of the Scottish National Party since 2014, Ms Sturgeon is the first woman to hold either position.
She has been a member of the Scottish Parliament since devolution started in 1999, initially as a regional list member for Glasgow before she won the Glasgow Govan constituency from Labour in 2007.
The 46-year-old lives in Glasgow with her husband, Peter Murrell, the SNP’s chief executive. She first met him at a Young Scottish Nationalists gathering in Aberdeenshire when she was 18.

The couple have been in a relationship since 2003 and married in 2010. They do not have any children, although she disclosed last year that she had a miscarriage in 2011.
Forbes magazine ranked her as the 50th most powerful woman in the world in 2016 and second in the UK in 2015.
She has put gender equality at the forefront of her political agenda, along with independence.
Ms Sturgeon is regarded as a “nippy sweety” in Glaswegian dialect, a prickly character who is difficult to warm to.
She and her advisers have worked hard to soften her image and she now appears much more empathetic, but she still appears to have little hinterland outside politics.
Background
Ms Sturgeon was born in Irvine, Ayrshire and is the eldest of three daughters born to her father, Robin, an electrician, and Joan, a dental nurse.
She grew up in Prestwick and Dreghorn, where her parents took advantage of Margaret Thatcher’s Right-to-Buy policy to purchase their council house for £8,000.
She joined the SNP at the age of 16 and, according to the SNP’s biography, has been “fighting independence ever since.”

Ms Sturgeon has attributed her choice of political allegiance to Mrs Thatcher’s controversial policies being forced on a population that had not voted for her. Thousands of jobs were lost following the impact they had on coal mining and steel production. Even before the SNP, she joined the Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament.
Ms Sturgeon read law at Glasgow University, where she was an active member of the Scottish Nationalist Association.
Following her graduation in 1992, she worked for firms of solicitors in Glasgow and Stirling.
She made several unsuccessful attempts to be elected a councillor, before unsuccessfully fighting the Glasgow Govan seat in the 1997 general election.

Rise to First Minister
Alex Salmond recognised Ms Sturgeon’s political talent at an early age and she started climbing the rungs towards political power following the creation of the Scottish Parliament in 1999, when she was elected as a regional list MSP for Glasgow under proportional representation. She was a high-profile member of the SNP’s Shadow Cabinet under both Mr Salmond and John Swinney, his successor.
After Mr Swinney resigned following a poor showing in the 2004 European elections, Ms Sturgeon announced she would stand for the leadership against Roseanna Cunningham, his deputy and the favourite to win. However, the contest was turned on its head when Mr Salmond announced he would stand for the leadership for a second time, with Ms Sturgeon as his deputy.
Although he won, he was still an MP at Westminster, leaving Ms Sturgeon with the high-profile role of leading the SNP group at Holyrood and taking on Labour’s Jack McConnell at First Minister’s Questions every week, a task at which she proved highly effective.
Ms Sturgeon finally got her hands on power in the 2007 Holyrood election after the SNP emerged the largest party by a single seat from Labour and formed a minority administration. She also won the Glasgow Govan constituency for the Scottish Parliament, taking it from Labour.
Mr Salmond appointed her Deputy First Minister and Health Minister in his first Cabinet. She won widespread praise for her handling of the 2009 flu pandemic.
Campaign for independence
The SNP won a majority at the 2011 election, a victory thought impossible under Holyrood’s complicated electoral system that prompted then Prime Minister David Cameron to offer an independence referendum.
Ms Sturgeon was appointed Infrastructure, Investment and Cities Minister with responsibility for the 2014 referendum. She played a high-profile role in the campaign, making a series of dubious claims about Scots enjoying another oil boom if they voted Yes and their NHS being privatised if they did not.
However, the nationalists still lost by 55 per cent to 45 per cent, prompting Mr Salmond’s resignation and Ms Sturgeon’s coronation as his replacement.
She was seen as a less divisive character than her predecessor and an extended political honeymoon, combined with the legacy of the independence referendum, saw the SNP win 56 of 59 Scottish seats in the 2015 general election.
The SNP also won last year’s Holyrood election under her leadership but lost its majority, forcing her to form another minority government.
Only hours after the Brexit vote was announced last June, she asked her civil servants to draw up legislation for a second independence referendum and issued a formal demand to Prime Minister Theresa May earlier this year, which was rejected.
Her demand prompted a backlash from those Scots tired of political upheaval and her poll ratings suffered. This now appears to have played out in the election.
Ms Sturgeon admitted she was "disappointed" by the results, but said she would not make any "rash decisions" on her plan for another independence vote.

What does the SNP want?
In one word - independence. In an interview last September, Ms Sturgeon admitted this “transcends” everything else for her, including Brexit and the economy.
This is demonstrated by the political make-up of the party, which includes some Right-wingers whose views are almost indistinguishable from those of the Tories on most issues, and many on the Left, some of whom used to be Labour Party members. They are united by their belief in an independent Scotland.

Increasing support for independence has also been the defining mission of the party in government. Their early years in power were marked by a series of eye-catching moves, such as re-branding the Scottish Executive as the Scottish Government and Scottish Cabinet ministers as Scottish Cabinet Secretaries, aping the UK Government’s terminology to make them appear equal.
They also announced a series of populist policies such as free prescriptions and university tuition for Scottish and EU students.
However, there have been few major reforms of public services, the education system or the NHS that threaten their popularity.
Ms Sturgeon has belatedly attempted to address declining standards in literacy and numeracy by introducing reforms that would give schools more autonomy from councils.
Who can vote for them?
Voters aged 16 and above who are registered in Scotland can vote for the SNP in Scottish Parliament and council elections, with the lower age limit 18 for next month’s general election.

Our manifesto: Real political insight, free for 30 days.
Rely on unrivalled insight and sharp analysis from our stellar team of Westminster insiders.
Join the most trusted voice in politics. Follow Election 2017 with Telegraph Premium.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
