Paralysed cyclist 'eating mash' again after brain implant connects thoughts with arm

Paralysed people could regain control of their own limbs, scientists have proven, after connecting a man’s thoughts to his arm muscles, allowing him to feed himself for the first time in eight years.
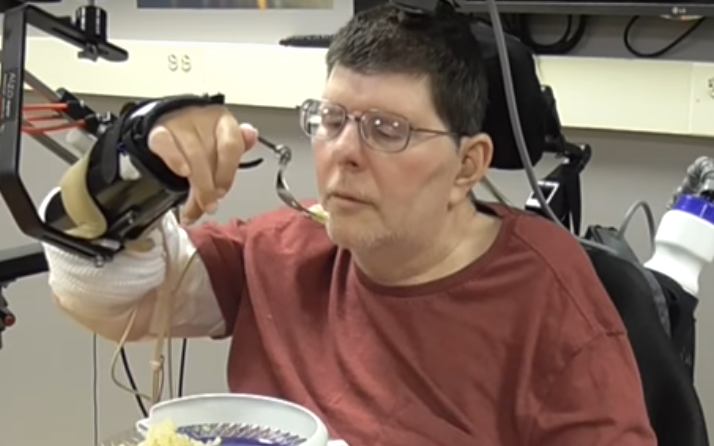
Bill Kochevar, 56, who was left paralysed from the neck down following a cycling accident, is now able to drink coffee, eat macaroni cheese and mashed potato and even scratch his nose with a loofah after being fitted with the groundbreaking technology.
The device works by sending Mr Kochevar’s brainwaves to a computer, where they are translated into electrical pulses and directed to electrodes implanted near the paralysed muscles in his arm and hand. As the muscles switch on they allow him to grasp objects and raise his arm.

He is the first person with quadriplegia in the world to have arm and hand movements restored using a direct link to the brain.
“For somebody who’s been injured eight years and couldn’t move, being able to move just that little bit is awesome to me,” said Mr Kochevar, 56, of Cleveland, Ohio. “It’s better than thought it would be. It’s pretty cool to be the first one in the world to do it.
“I’m making it move without having to really concentrate hard at it. I just think ‘out’ and it goes.”
The device was developed by scientists from Case Western Reserve University, who are based at the Cleveland Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) Center in Ohio.
Mr Kochevar became paralysed in 2009 during a 150 mile charity bike race when a postal van that he was riding behind stopped suddenly to deliver a package, and he went into the back. For the past eight years he has relied on carers to help him with every task, but now has the first hope of independence.
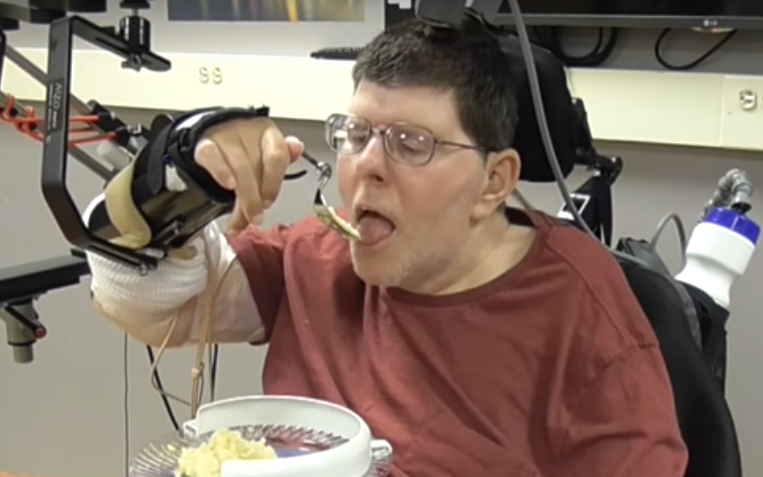
“People have to do stuff for me that I can’t do myself. They have to turn my every two hours, if I want water, they have to get me water. This research has enhanced my ability to be able to do things,” he added. “Now we can tell the world it is possible to reconnect the brain and make the arm move again. I ate a pretzel, it really got good one day I had some mashed potato.”

A team of surgeons implanted two electrode arrays, each around the size of a baby aspirin, on the surface of Mr Kochevar’s brain to record signals when he imagines moving his own arm and hand.
That signal is then fed into a computer which turns the command into an electrical pulse which triggers 36 electrodes in his hand, wrist, arm, elbow and shoulder. To overcome gravity that would otherwise prevent him from raising his arm, Mr Kochevar also a mobile arm support, which is also under his brain’s control.
After 45 weeks of training Mr Kochevar can now move each joint in his right arm independently just by thinking.
“By taking the brain signals generated when Bill attempts to move, and using them to control the stimulation of his arm and hand, he was able to perform personal functions that were important to him,” said Dr Bolu Ajiboye, assistant professor of biomedical engineering and lead study author.
“Although similar systems have been used before, none of them have been as easy to adopt for day-to-day use and they have not been able to restore both reaching and grasping actions
“With further development, we believe the technology could give more accurate control, allowing a wider range of actions, which could begin to transform the lives of people living with paralysis.”

When asked, people with quadriplegia say their first priority is to scratch an itch, feed themselves or perform other simple functions with their arm and hand, instead of relying on caregivers.
“Every day, most of us take for granted that when we will to move, we can move any part of our body with precision and control in multiple directions and those with traumatic spinal cord injury or any other form of paralysis cannot,” said Dr Benjamin Walter, associate professor of Neurology at Case Western
“The ultimate hope of any of these individuals is to restore this function. By restoring the communication of the will to move from the brain directly to the body this work will hopefully begin to restore the hope of millions of paralyzed individuals that someday they will be able to move freely again.”
And the devices could soon be available outside of the lab. Work is underway to make the brain implant wireless, and the scientists are improving decoding and stimulation patterns needed to make movements more precise.
“This is a major step toward restoring some independence,” said Dr Bob Kirsch, chair of Case Western Reserve’s Department of Biomedical Engineering.
“He’s really breaking ground for the spinal cord injury community,”
The research was published in The Lancet.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
