The pregnant migrants risking life and limb to give birth on a French island colony
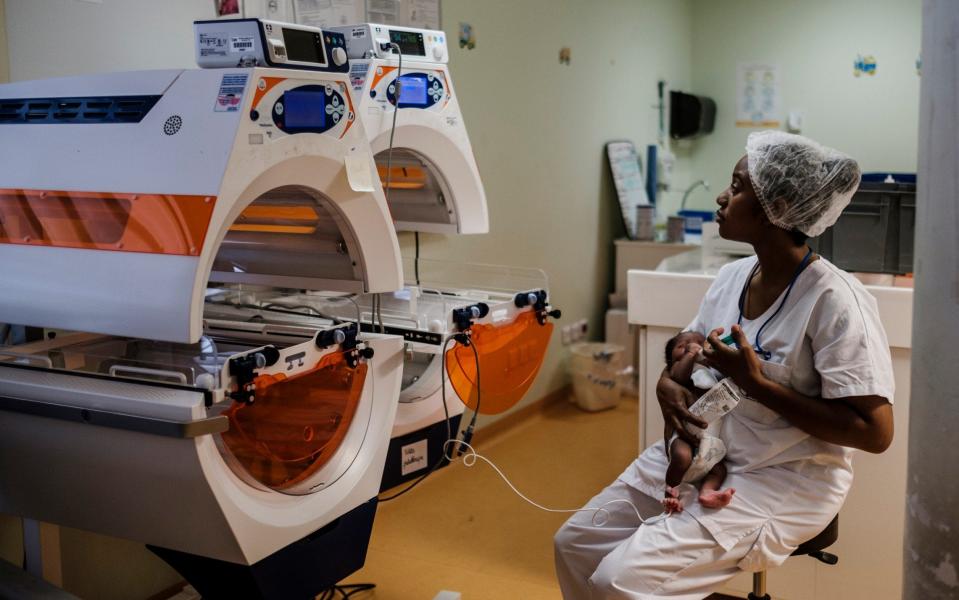
At first glance, there is little that seems extraordinary about the hospital that risks being cut out of a country.
Save for the palm trees in its grounds or the dramatic views across volcanic hills and reef-bound lagoons, it could be a health facility just about anywhere in the First World.
Yet the Central Hospital of Mayotte (CHM) has a story like no other: bitter political rows have been fought over it, people have died in droves trying to reach it and Marine le Pen, the nationalist politician, has acquired a devoted following among a group of black French Muslims in part because of it.
The CHM boasts a singular claim to fame that is at the root of all these passions. Of all the hospitals in the European Union, none delivers as many babies – even though it is situated on a French island colony off the east African coast.
It is not a statistic that the hospital’s overworked staff are proud of, however, for the record is eclipsed by another: Seventy per cent of the mothers giving birth on its maternity ward are foreign, most of them illegal migrants hoping that their children will gain French citizenship by being born on French soil.

In recent years, Europe’s leaders have been preoccupied by a migrant crisis that has brought tragedy to the Mediterranean, polarised politics and galvanised the far right.
Yet, little noticed on the continent, another European migrant crisis has unfolded in the Indian Ocean, where tens of thousands every year risk their lives crossing shark-infested waters to reach a tiny and overburdened patch of EU soil thousands of miles from Europe. For many, the CHM is their target.
As pagers bleeped urgently and doctors scurried from baby to baby on a maternity ward that delivers 25-35 infants a day, a hospital administrator surveyed the scene.
Her doctors were there to provide assistance to whomever needed it, regardless of whether or not they were in Mayotte legally, but they were being overwhelmed.
“The quality of health care we are able to provide is deteriorating,” she said. “It cannot continue like this. We have to find a solution.”
Mayotte is an oddity. Africa’s Winds of Change blew late into the Comoro Archipelago. It was only in 1975 that three of its four islands voted to break away from French rule and form the Union of Comoros.

But Mayotte, the fourth, with deeper historical ties to France, declined to throw off French overlordship.
Four decades later, the fortunes of the two Comoro territories could not be starker.
As Comoros became one of Africa’s poorest states, wilting under misrule, insecurity and 21 coup or coup attempts in 43 years, Mayotte prospered, at least relatively.
Its people may only earn a third of what their fellow citizens in metropolitan, or mainland, France do, but they are still 14 times richer than their Comorian former countrymen.
That gap is only likely to grow, with Mayotte qualifying for additional funding from Paris and the EU after formally becoming a French department in 2011.
Little wonder, then, that Mayotte has become a lure for Comorians desperate to swap immiseration for French benefits, French citizenship and a French way of life.
“For people living on the other islands, Mayotte looks like the United States,” said Kamal, a journalist on Anjouan, the closest of the three Comorian islands to Mayotte.

Life on Anjouan is precarious and tough. Two thirds of the working age population is unemployed. Most subsist on tiny farms. Last month, a mysterious band of gunmen seized control of the centre of its main town, Mutsamudu, prompting fresh repression from an unpopular, authoritarian government.
For the people of Anjouan, escape from all this is tantalisingly close. From its southern shores, Mayotte – with its free healthcare and education – is just 40 miles away. Every night gaggles of Comorians gather in the moonlight to make the dangerous, illegal and expensive crossing.
An average of ten fibreglass boats – known locally as kwasa-kwasa – strike out for Mayotte every day.
Some do not make it. Human rights groups estimate that as many as 20,000 Comorians – 2.5 percent of the country’s 800,000 population – have drowned in these waters since 1995, largely because the boats are often overcrowded and unseaworthy, one kwasa-kwasa captain said.
Even so, migrants are willing to pay 400 euros for a one-way ticket.
“There is little here,” the captain shrugged. “There, there is the promise of life.”

A large proportion of the migrants are pregnant women, trying to make their way to the CHM.
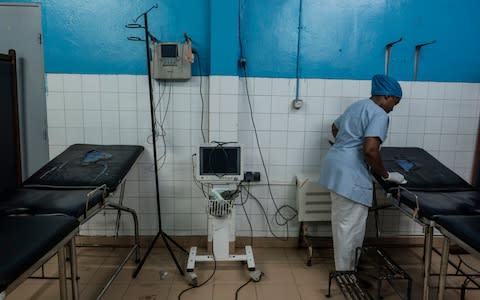
Given the challenges facing health facilities in Comoros it is not hard to see why. The maternity ward at Hombo hospital, the main referral facility on Anjouan, has just two threadbare obstetric beds and, at least when The Telegraph visited, no patients. There are few skilled doctors on the island and patients have to pay for their services.
The contrast with Mayotte’s main hospital, with its neat signposts pointing to childhood psychiatric wards and dental units, sanitised corridors and state-of-the-art incubators, could not be more striking.
But the CHM is visibly under strain. According to official French statistics, three-quarters of the 9,800 babies delivered last year were born to foreign mothers.
The maternity ward’s waiting room heaved with pregnant women, some resting their heads against walls to alleviate the contraction pains. Most, the staff reckoned, were Comorian.
For these mothers, the CHM not only offers a free, safe delivery, it also means their children can gain the most sought after prize of all: a French passport, made possible by a law that sets children born on French soil on the path to citizenship.
For Ahmada Moustafa, that passport opens up a world of opportunities for Aymen, her three-day-old son in the cot next to her.
“He will be able to work, he will have prospects,” she said. “He will be able to do far more things in life than I ever could.”
Unlike many in the waiting room, Mrs Moustafa was not fresh off a kwasa-kwasa. She has been on Mayotte for 23 years, since arriving from Comoros at the age of two.
But until she recently acquired residency status, she had been an illegal immigrant, spending much of her life in hiding, too scared to leave her sprawling migrant slum lest she be caught by the police.

Those slums are growing every day.
Of the 256,000 people crammed onto Mayotte’s 144 square miles, more than half are foreign and 42 percent are there illegally.
A backlash has been inevitable, even though Mahorans – as the people of Mayotte are known – share much the same ethnicity, the same language and the same Muslim faith as the Comoran migrants.
So grave is the strain on public services that many schools have to operate two shifts a day. A growing number of Mahorans now choose to have their children privately educated. Mothers are increasingly giving birth in metropolitan France.
For those Mahorans who choose to deliver at the CHM, the resentment is palpable.
“Because there are so many Comorian mothers in here, the Mahorian mothers don’t get the kind of attention we pay our taxes for,” said Nema, a Mahoran woman and the mother of two-day old twins.
“I wanted an epidural but I couldn't get one because the anaesthetist was too busy.”

The French government has struggled to contain the anger. Anti-migrants protests have roiled the island this year, while Marine le Pen won 43 percent of the vote in last year’s presidential election after visiting the island to champion tough anti-immigration policies – an extraordinary showing in France’s most Muslim region.
Emmanuel Macron’s government has considered radical solutions to the crisis, including a cabinet proposal to give the CHM extra-territorial status, excising it from France to stop babies born there from qualifying for citizenship.
In September, France passed a law requiring the parents of babies born in Mayotte to have been resident there for at least three months.
Such measures will do little to stem the tide, many Mahorans fear. In the meantime, the authorities on Mayotte have stepped up deportations, expelling 18,000 illegal migrants this year alone – nearly as many as mainland France.
By denying them due process – many are deported within hours of reaching Mayotte – basic migrant rights have often been violated, according to Cimade, a migrants’ advocacy group.

“French law has to be applied here in the same way as it is in metropolitan France,” said Solene Dia, Cimade’s regional project manager. “Refugees must have the same rights here that they do in France.”
Legal issues aside, the deportations often seem to have little effect.
In the migrant slum behind the town of Vahibé, just a few miles from the trendy waterfront in the capital Mamoudzou, children bathe in a foetid stream near alleyways lined with corrugated iron shacks.
Most of those living here are in Mayotte illegally. If they venture out of the slum, they risk arrest and deportation.
Yet even if they are caught, getting back to Mayotte is not so difficult. For every kwasa-kwasa intercepted by the police, four make it through, locals reckon. Abdallah Ahmed has been deported to Anjouan ten times, but has returned each time, determined to be reunited with his children and because life, even in Vahibe, is better than it is at home.
“Over there is a dangerous dictatorship,” he said. “Life here may be hard, but at least I can go to hospital and my children can go to school. I put up with it all for their sake.
“I would rather die in Mayotte than live on Anjouan.”

Protect yourself and your family by learning more about Global Health Security

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 