Robot with ‘fettuccini-like fingers’ built by Harvard to catch jellyfish
Catching jellyfish is no easy task. For a start they are around 95 per cent water, and are one of the most delicate creatures in the oceans, easily damaged by nets and adept at slipping away from grasping gingers.
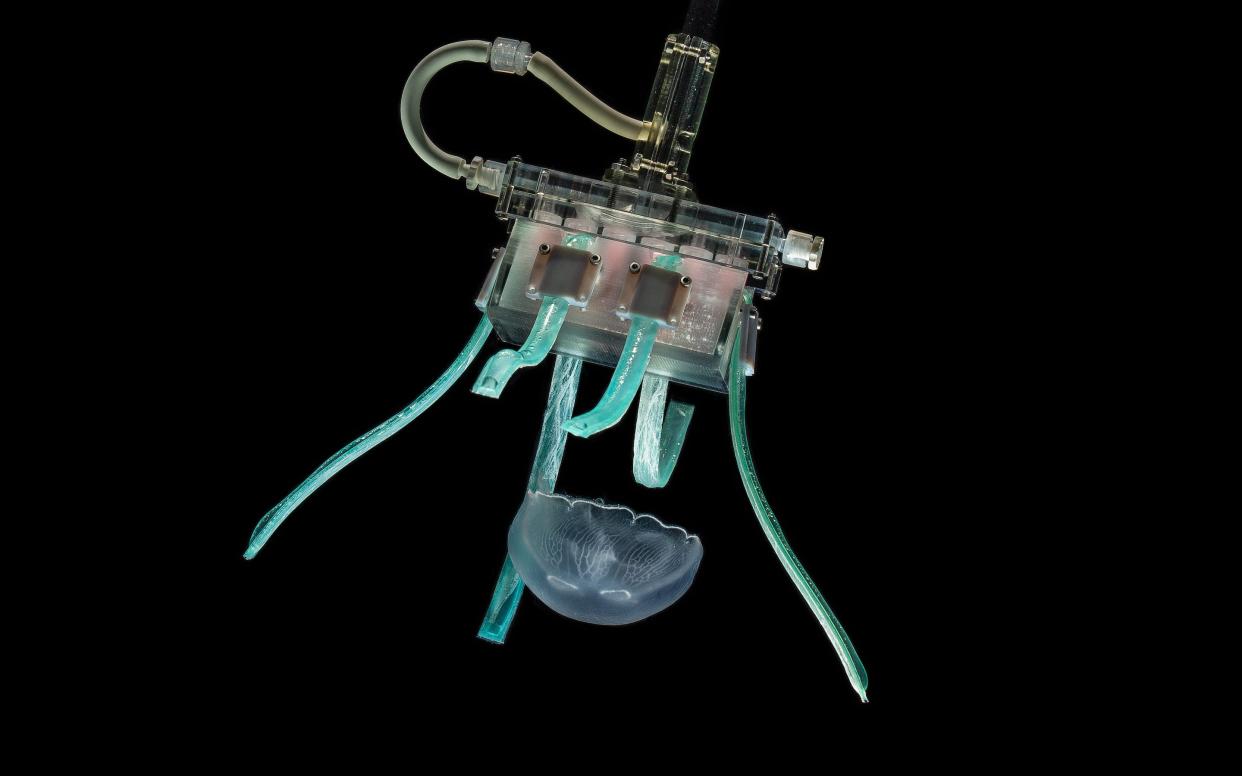
Now researchers at Harvard University have developed a robot which has ‘fettuccini-like fingers’ to clasp the little creatures in a gentle embrace.
Jellyfish are crucial for science, yielding important discoveries, such as green flourescent proteins which are used to study gene expressions. They also have fascinating life-cycles where they can actually reverse the ageing process.
Researchers believe that studying them could provide insights into to turn back the clock for humans.
But acquiring enough for studying has proved tricky and most remote underwater vehicles are designed for grasping rocks or hardier sealife.
The new gripper, designed by the Wyss Institute at Harvard uses hydraulic pressure to gently but firmly wrap its fingers around a single jellyfish, then release it without causing harm.
"Our ultra-gentle gripper is a clear improvement over existing deep-sea sampling devices for jellies and other soft-bodied creatures that are otherwise nearly impossible to collect intact," said first author Dr Nina Sinatra, Ph.D., a former graduate student at the Wyss Institute who is now a mechanical and materials engineer at Google.
"This technology can also be extended to improve underwater analysis techniques and allow extensive study of the ecological and genetic features of marine organisms without taking them out of the water."

The gripper's six fingers are made from thin, flat strips of silicone with a hollow channel inside bonded to a layer of flexible but stiffer polymer nanofibers.
The fingers are attached to a rectangular, 3D-printed plastic "palm" and, when their channels are filled with water, curl in the direction of the nanofiber-coated side.
The researchers fitted their ultra-gentle gripper to a specially created hand-held device and tested it on an artificial silicone jellyfish in a tank of water to determine the positioning and precision required to collect a sample successfully, before moving on to the real thing at the New England Aquarium, where they used the grippers to grab swimming moon jellies, jelly blubbers, and spotted jellies, all about the size of a golf ball.
The gripper was successfully able to trap each jellyfish against the palm of the device, and the jellyfish were unable to break free from the fingers' grasp until the gripper was depressurized.
The jellyfish showed no signs of stress or other adverse effects after being released, and the fingers were able to open and close roughly 100 times before showing signs of wear and tear.
"Marine biologists have been waiting a long time for a tool that replicates the gentleness of human hands in interacting with delicate animals like jellyfish from inaccessible environments," said co-author Dr David Gruber, Ph.D., who is a Professor of Biology and Environmental Science at Baruch College, CUNY and a National Geographic Explorer.
"This gripper is part of an ever-growing soft robotic toolbox that promises to make underwater species collection easier and safer, which would greatly improve the pace and quality of research on animals that have been under-studied for hundreds of years, giving us a more complete picture of the complex ecosystems that make up our oceans."
The research was published in the journal Scientific Reports.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
