The robotic brain surgeon will see you now: drill can perform complex procedures 50 times faster
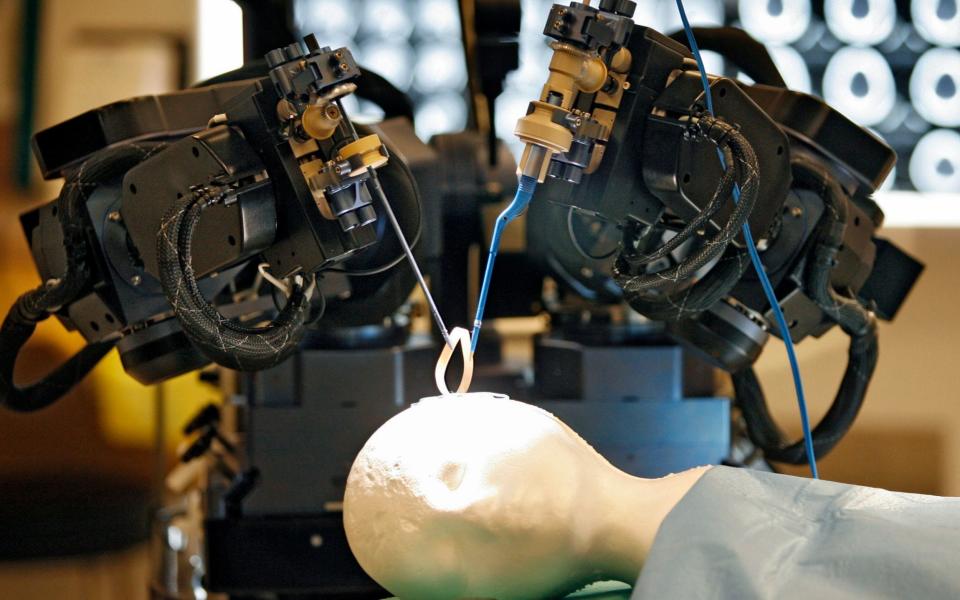
Scientists have revealed a robotic drill that can cut the most sensitive brain surgery down from two hours to two and a half minutes.
The machine, developed at the University of Utah, is being hailed as a potential breakthrough in survival for brain patients as the reduced time they spend in surgery will drastically cut the chances of infection.
Researchers say can make one type of complex cranial surgery 50 times faster than standard procedures.
We knew the technology was already available in the machine world, but no one ever applied it to medical applications
Dr William Couldwell, University of Utah
They say the drill produces fast, clean, and safe cuts, reducing the time the wound is open and the patient anaesthetized, which also decreases the chances of human error, as well as the cost of surgery.
In complex surgeries, especially cranial surgeries, surgeons typically use hand drills to make intricate openings, adding hours to a procedure.
Dr William Couldwell, neurosurgeon at University of Utah, she said: "It was like doing archaeology. We had to slowly take away the bone to avoid sensitive structures.
“We knew the technology was already available in the machine world, but no one ever applied it to medical applications."
Under the new system, patients will undergo CT scans to establish the exact location of sensitive structures such as nerves, major veins and arteries that must be avoided.
Surgeons use this information to program the cutting path of the drill and the surgeon can program safety barriers along the cutting path within 1 mm of sensitive structures.
Dr A.K. Balaji, who also worked on the drill, said: "The software lets the surgeon choose the optimum path from point A to point B, like Google Maps.
"Think of the barriers like a construction zone. You slow down to navigate it safely."
The drill does the heavy lifting by removing most of the bone, similar to a mill, accurately and rapidly.
It has so far not been tested on a human patient.
The research was published in the journal Neurosurgical Focus.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 