Treatment revolution for patients with multi-drug resistant TB
Daily injections for people with the most complicated form of tuberculosis could become a thing of the past under new treatment guidelines for this highly infectious lung disease.
The standard treatment for multi-drug resistant TB (MDR-TB) is arduous, with patients facing painful daily injections for six months or more, as well as taking a cocktail of sometimes toxic pills for around two years. Adherence to such a difficult regime is poor, with side effects including permanent deafness, psychosis and kidney problems.
Now, new treatment guidelines from the World Health Organization state that injections should be replaced with oral treatments such as bedaquiline, the first drug specifically developed for the treatment of MDR-TB.

Soumya Swaminathan, WHO deputy-director general for programmes, said: “The treatment landscape for patients with MDR-TB will be dramatically transformed for the better with the announcement today.”
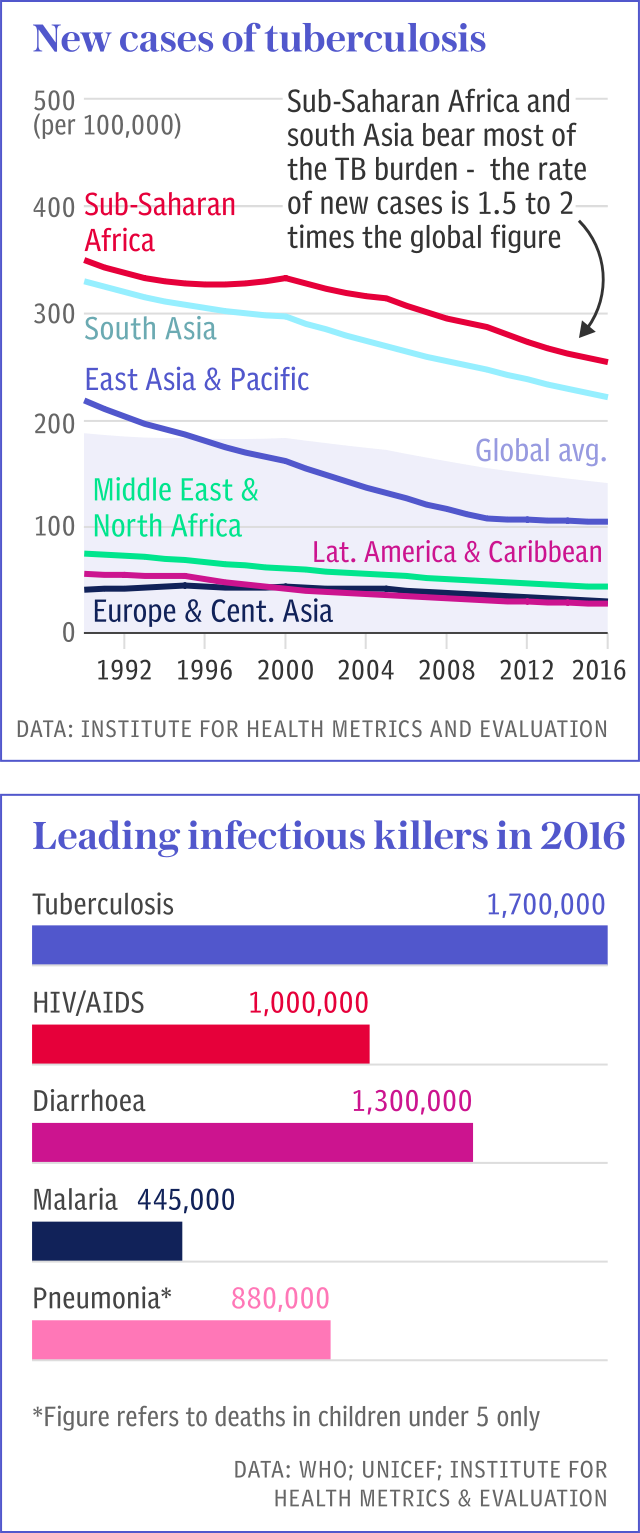
According to the latest figures from WHO there were around 340,000 new cases of MDR-TB diagnosed in 2016, with around half of these cases occuring in India, China and Russia.
WHO's announcement comes a month before the first ever high level United Nations meeting on TB, where world leaders will discuss how to wipe out this infectious disease which claims an average of 4,500 lives every day.
Aaron Oxley, executive director of campaigning organisation Results UK, welcomed the new guidelines.
"This is great news for the hundreds of thousands of people with drug-resistant strains of TB, removing the need for toxic drugs whose gruelling side effects can cause deafness, psychosis and permanent nausea. But the battle isn't over; access to these newer treatments remains hugely limited and people with TB will rely on countries updating policies and stepping up their investments at the forthcoming UN high-level meeting," he said.
Médecins Sans Frontières also welcomed the new guidelines but urged Johnson and Johnson (J&J), manufacturers of bedaquiline, to cut the price of the drug to ensure it is available to those in the poorest countries.
“Governments and treatment providers should not waste another minute and should urgently make sure people can access optimal treatments including bedaquiline, and this means J&J needs to lower the price of the drug and ensure it is available for every person who needs it,” said Dr Mercedes Tatay, MSF’s international medical secretary
J&J recently announced a price reduction for bedaquiline in some countries meaning it now costs $400 for six months of treatment. But MSF, alongside other organisations, would like to see the price go down to $192 for a six-month treatment.
The experience of patients in Papua New Guinea - where 3.4 per cent of all new cases and 26 per cent of all previously treated cases of TB are multi-drug resistant - shows the need for new treatment regimes.
Dr Rendi Moke, TB specialist at Port Moresby General Hospital in the country’s capital, has recently introduced a new, shorter treatment for patients with multi-drug resistant TB.
“The previous treatment was around 24 months or more, we lost patients to follow up and had difficulty retracing them and bringing them back to ensure they completed their course,” he said.
Patients have to stay in a special isolation ward and are isolated from their communities, and even though this programme is shorter than the standard treatment, not all patients stick to it, said Dr Moke.
“You cannot half treat a TB patient,” he said.
Protect yourself and your family by learning more about Global Health Security

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 