Trump versus Twitter: How the President's social media clampdown could change the internet

It’s not unusual for Donald Trump to wage war against someone on Twitter, but this time he is looking to bring down the company itself.
On Thursday, the US President signed an executive order to “prevent online censorship,” just days after he threatened to "shut down" the company after becoming enraged that it added a fact-checking label to one of his tweets.
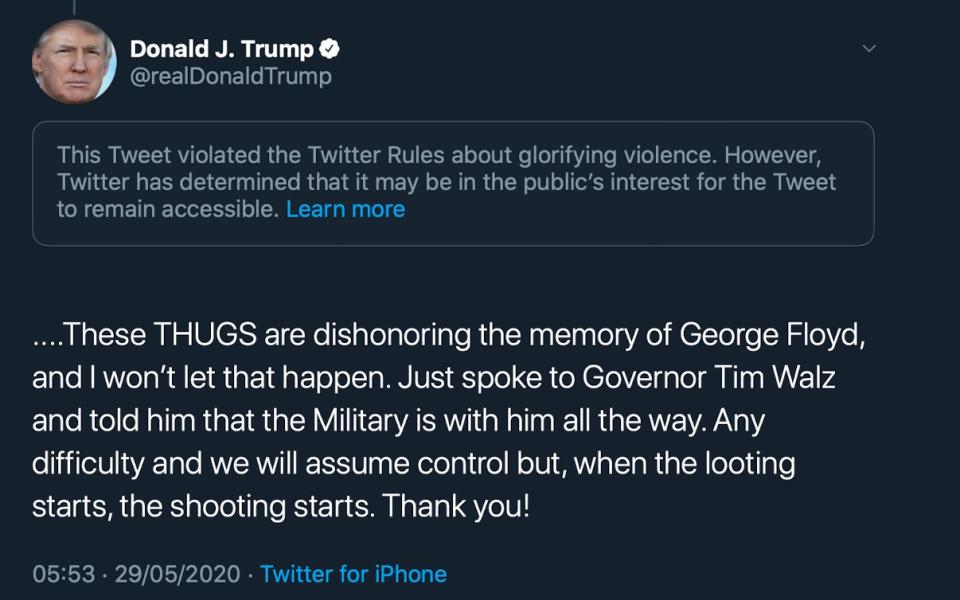
On Friday morning, Twitter struck again, flagging another of Trump's tweets and hiding it from view, this time for "glorifying violence" amid protests against the death of George Floyd.
The President's Tweet said: "These THUGS are dishonoring the memory of George Floyd and I won't let it happen... Any difficulty and we will assume control but, when the looting starts, the shooting starts."
The executive order, which Trump claims will stamp out alleged anti-conservative bias, could drastically impact how companies like Twitter, Facebook and YouTube can moderate content on their platforms, potentially limiting their ability to remove harmful or misleading content for fear of losing a privilege that shields them from being sued.
These privileges, enshrined under Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act, a 1996 law on which the modern web has been built, currently gives social media companies the ability to moderate speech while maintaining that they are not legally responsible for comments posted by users, unlike traditional media publishers.
Should social media companies do anything to discriminate against users by removing their posts or block their accounts without a fair hearing, this privilege should be revoked, the order says.
Critics say this will lead to the order, as it is written, having the opposite effect of which it intended, forcing social media to crack down harder on comments and posts.
There is NO WAY (ZERO!) that Mail-In Ballots will be anything less than substantially fraudulent. Mail boxes will be robbed, ballots will be forged & even illegally printed out & fraudulently signed. The Governor of California is sending Ballots to millions of people, anyone.....
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) May 26, 2020
"It will restrict more speech online, not less," a Facebook statement released shortly after the order was published read.
Twitter called it a "reactionary and politicised approach" that would "threaten the future of online speech and internet freedoms".
This EO is a reactionary and politicized approach to a landmark law. #Section230 protects American innovation and freedom of expression, and it’s underpinned by democratic values. Attempts to unilaterally erode it threaten the future of online speech and Internet freedoms.
— Twitter Public Policy (@Policy) May 29, 2020
However, there is one major stumbling block: Trump can’t change the law through his executive order - only Congress, the US legislature, has that power. Instead, the executive order calls on US regulator the Federal Communications Commission to reinterpret it.
Among other issues, lawyers argue that the FCC and consumer regulator the Federal Trade Commission do not regulate social media. On Thursday Jessica Rosenworcel, one of the FCC's five commissioners, said the order “does not work”.
It is also not clear whether the order actually has any legal force. Lawyers argue that the President’s change in interpretation of the law is unlikely to stand up in court.
The order published on Thursday says that “the scope” of companies’ immunity under the law “should be clarified”.
It says social media platforms must act in “good faith,” and if they “remove or restrict access to content” in a way which is “deceptive or pretextual”, they forfeit their protection from being considered publishers.
In addition, the order, which covers all social media platforms including Facebook and Google’s YouTube among others, proposes restricting US government advertising spending on social media companies that are found to violate free speech. It says the Federal Trade Commission and individual states should also review the law.
.@Twitter is now interfering in the 2020 Presidential Election. They are saying my statement on Mail-In Ballots, which will lead to massive corruption and fraud, is incorrect, based on fact-checking by Fake News CNN and the Amazon Washington Post....
— Donald J. Trump (@realDonaldTrump) May 26, 2020
What is Section 230?
The 24-year-old law that Trump wants to change has long been a shield for internet companies, allowing them to host a wide variety of opinions, some of them offensive, without being sued. It also lets them moderate their sites without becoming responsible for the content.
The law came about as a result of a lawsuit brought by brokerage firm Stratton Oakmont (now fictionalised in the Leonardo DiCaprio film The Wolf of Wall Street) against an internet service provider, Prodigy, which had hosted anonymous comments accusing the firm of fraud. The New York Supreme Court said Prodigy was technically a “publisher”, because it had moderated content. But two Congressmen recognised the danger posed by the ruling and in 1996 introduced a law allowing websites to set rules for the content they host without becoming legally responsible for all of it.
While a true publisher, such as a newspaper, is held liable for everything it prints, Section 230 places social media sites somewhere closer to libraries or newsstands, which are protected from responsibility for hosting or promoting other people’s words.

It has since helped social media firms escape legal judgment for a wide variety of things.
Last year the US court of appeals ruled that Facebook was not responsible for violence coordinated and incited by accounts linked to Palestinian Islamist militant group Hamas, citing the law.
Supporters of Section 230, including social media companies, argue that it actually enables the constitutional American right to free speech, because it means that technology companies can host legally dicey content without the fear of being held responsible.
Without the ability to moderate without fear of incurring legal penalty, they argue, the internet would either be a chaotic, abuse-filled, unworkable free-for-all or much more tightly regulated by companies who would fear the legal consequences of missing a legally problematic post.
The industry has rallied together to condemn the order, arguing that it will do far more harm than good.
Jon Berroya, head of the Internet Association, the trade union representing technology heavyweights like Google, Amazon, Facebook, pointed out that claims of bias “rely on isolated anecdotes that are undermined by the fact that politicians and political groups successfully use social media to reach millions of followers every day”.
He warned that revoking Section 230 would “undermine a variety of government efforts to protect public safety and spread critical information online”.
There’s also the argument that while large internet companies like Facebook and Twitter have the money and resources to defend themselves, any greater liability would be more onerous for smaller startups, potentially stifling competition in the industry.
Trump’s attack is only the latest in a series of changes which reduced the scope of the law. Backpage.com, a site which hosted many adverts for sexual services had repeatedly managed to defend itself from cases brought by trafficked women and girls and their families using section 230, until a law was brought in in 2018 to limit the immunity of sites which were “knowingly hosting third-party content that promotes or facilitates sex trafficking”.
In the US, politicians across the political spectrum have also criticised the law. Critiques from Democrats usually focus on harassment and content which is racist or otherwise offensive, with the argument that tech companies aren’t dedicated enough to removing it because of their immunity.
Right-wing politicians have argued that it empowers tech companies to stifle free speech by removing opinions that they don’t like.
'Conservative bias'
It may have become the unofficial, and most regular, means of communication between the White House and the outside world, but Trump and Twitter have a chequered history.
Mr Trump’s latest attack on social media emerged after Twitter attached a warning to some of his tweets which prompted users to fact check his claims.
The tagged tweets included claims about postal voting, which have since been debunked. Mr Trump claimed that the mail-in ballots lead to vote fraud and ineligible voters getting ballots. Hours later he warned, on Twitter, that he would regulate social media companies, or “shut them down”.
And on Friday, as amid violence and protests against police brutality following the death of George Floyd in Minneapolis, Trump Tweeted again. "When the looting starts, the shooting starts," he said.
Twitter tagged this Tweet as being against its rules and hid it from view or further re-tweets.
Twitter's warning said: "This Tweet violated the Twitter Rules about glorifying violence. However, Twitter has determined that it may be in the public's interest for the Tweet to remain accessible." Users had to clock through a content-warning to view the post.
But the president accused the company of bias during the 2016 election and of “shadow banning” in 2018, when several Republicans’ accounts were blocked from appearing in the Twitter search bar. Jack Dorsey, Twitter’s co-founder, later apologised and claimed that it was down to a glitch. He has also accused Google of "rigging" its search engine.
In the same year, Dorsey, who recalls opposing political views being discussed across the dining room table in the home he grew up in with his Democrat mother and Republican father, was grilled during a Congressional hearing on bias, in which he denied that the app and website’s automated moderation systems leaned a certain way.

Twitter was also threatened with a US Department of Justice investigation to assess whether social media companies were stifling free speech.
Whether the order will materialise into anything other than words seems unclear. Hypothetically, it could cause Twitter or Facebook to scrutinise Mr Trump's tweets more carefully if they need to police content to avoid legal battles.
But rumours of a legal challenge to the order from the tech industry were already mounting on Thursday. By fact-checking the President in the first place, Twitter knew it was getting into a fight. It is unlikely to back down now.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
