The estate that 'blew up' its last link to Manchester
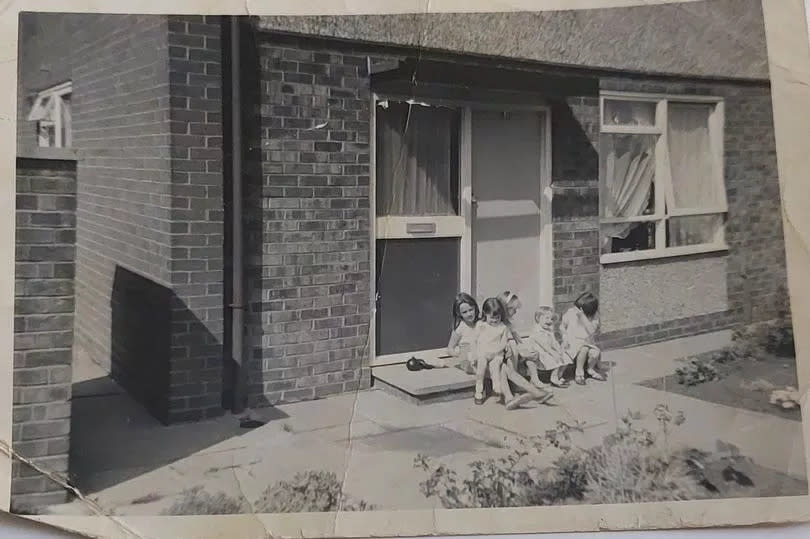
For Maria Murphy her new home was 'like a palace'. Having moved from a post-war prefab bungalow in Blackley, just the fact of having stairs seemed exotic and exciting to the then 10-year-old.
"I just thought it was fabulous being able to go upstairs to bed," said Maria. "It was so, so different to where we'd come from."
In 1962, Maria, her two sisters and their parents became one of the first families to move onto Darnhill in Heywood, then a Lancashire town. It was one of several overspill estates built by Manchester council during the slum clearances of the 1950s and 60s.
But while Maria's new living arrangements were certainly up to scratch, the same couldn't be said for the rest of the estate. "When we moved in it was still being built," said Maria.
READ MORE:
READ MORE:
"There were no pavements yet, it was like these cinder paths and there was no school so I had to catch the train to Moston with my mum while she went to work, then walk to Blackley. But it was a kids' paradise. We used to play on the building sites and get told off all the time."
The idea for Darnhill was first proposed in 1950. 'Plan to accommodate Manchester people in Heywood', ran the headline in the Heywood Advertiser, on March 3 that year.
Two years later, 171 acres of land to the west of Heywood, mainly fields and some farm buildings, some eight miles from Manchester, was identified as a potential site for what was being described as an 'overspill development'. But the plans met with opposition from the off.

A public inquiry was called and many local objections were raised, including from local farmers who feared losing their livelihoods. But those concerns were overruled and, in 1956, the government approved the compulsory purchase of the land.
The plan was to build 1,236 two-storey houses, 594 flats, and 20 bungalows homing around 8,000 people, who would be moving largely from the inner-city districts of north Manchester, such as Miles Platting, Collyhurst and Blackley.
At the time around 24,000 people lived in Heywood, meaning the new estate would increase the town's size dramatically. And, initially at least, the new-comers weren't exactly welcomed with open arms.
"The local people didn't want the estate to be built," said Maria, whose surname is now Bartlett. "There was a stuck up attitude to it being a council estate. They used to call us the 'Hillbillies' and at school they'd sing a song that went 'Those Darnhillians, darn right silly uns'.
"They used to say the fresh air would do us good, because they thought we'd come from this dreadful place, from the slums. It wasn't Buckingham Palace but it certainly wasn't a slum."
And the frosty reception was compounded by the huge upheaval the new 'Darnhillians' were experiencing. "At first there was a sense of loss, because everybody had been brought up on streets where your auntie lived next door and your grandma was round the corner," said Maria.
"But we were all in the same boat. We'd all come from the same places and had the same experiences, so when everybody started to settle in, we started helping each other and made a new community."

Most of the men building the estate were Scottish, which led to Darnhill's Caledonian-themed street names such as Dunblane Grove and Dumbarton Drive. And soon shops, schools, churches, a library and a community centre were built for the new community.
The first school to open was Darnhill County Primary, which originally had just three pupils. As more and more families moved onto the estate, Our Lady & St Paul's Infant and Junior School opened in April 1963, followed by St Margaret's C.E. Junior School in January 1964. Two churches, St Margaret's and Our Lady & St Paul's were also built, while Sutherland High School opened in 1966.
Every good estate needs a good estate pub. And Darnhill had two - the Criterion and the Highlander. Damien Sugden, 57, grew up as one of nine children on Birnam Grove and remembers the Criterion as being at the centre of life on Darnhill.
"My grandad, Frank Lutkevitch, lived behind us and his back garden backed on to ours," he said. "We made a passageway linking the two gardens and every night at 9.15pm he would walk through, sit in our house for 10 minutes and then carry on with his walk to the Criterion for his bottles of Guinness.
"The Criterion was a great place to go as long as you knew someone in there. There were some real characters, proper Manchester people with a cutting wit.
"I have been with my wife 30 years and we still laugh about our first date. I took her in the vault of the 'Cri' and basically got the micky took out of me, but we had a brill night and she still carried on seeing me."
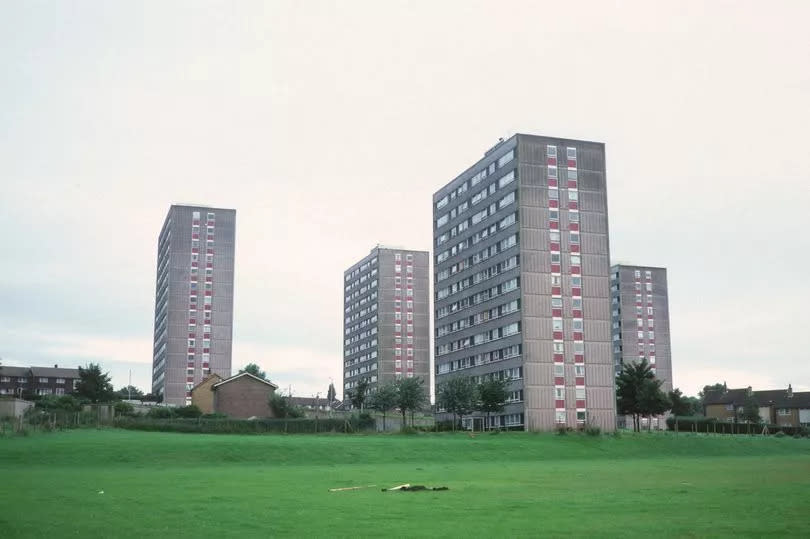
In 1963 the construction of nine 13-storey tower blocks on Darnhill, at a cost of £1.6m - £40m in today's money - was approved. In remarkably quick fashion the first block was completed later that year, transforming the Heywood skyline.
They were the first British flats built by the French-developed Sectra system, which would go on to be used in developments in Hulme, Smethwick, Sunderland and Rathcoole. That year a British Pathe news crew would visit Darnhill to film the pioneering construction technique in action.
And at first the flats were highly-sought after. "The best years of my life were living on Darnhill when these high rises were up," a former Armadale and Dunvegan Court resident wrote on the Tower Block website.
"The flats themselves were spacious and comfortable and the views depending on which floor you lived on were fantastic, you could see for miles and many an evening I would stand on my balcony watching the world go by."
But, in a situation repeated on post-war estates across the UK, as the 60s moved into the 70s and 80s, the flats fell in disrepair as government priorities changed and local council funding was slashed. On Darnhill the situation was exacerbated by the jumble of who was actually responsible for what.
Darnhill was owned by Manchester council, who collected the rent, yet tenants paid their rates to Rochdale council. "To Manchester it was a remote overspill estate and not even in Manchester," a former Darnhill resident said.
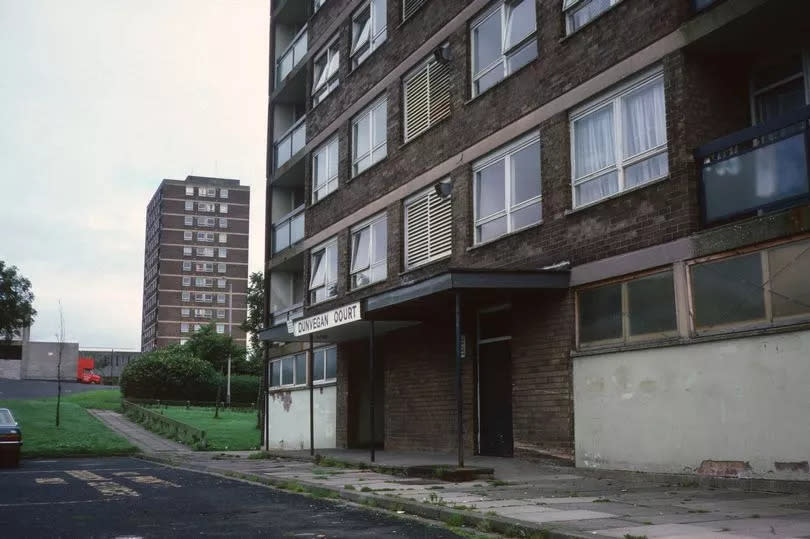

"Rochdale council had to maintain the roads, but to them, it's not their estate." Soon Darnhill was being dubbed a 'no-go' estate as vandalism and crime soared.
Complaints that the high-rises had become a 'dumping ground for yobs' made headlines in the Heywood Advertiser. Bus drivers threatened to boycott the estate after dark.
"In the mid 80s, we lived in Armadale Court on the 12th floor," one former tower block resident said. "There were no caretakers.
"Lads were even keeping their motorcycles in the flats, via the lifts and were revving them up. Drunks and yobs took over and most people became more reclusive.
"The lifts were in decline and used as toilets. The council did not vet who they let live in the flats and it sealed the death of them."
By the late 90s many of the flats were unoccupied. Unhappy with how Manchester council were running the estate more than 90% of Darnhill residents voted in favour of transferring the management to housing association Guinness Trust.

One of the first things the trust after taking over did was order the demolition of the flats. Over the next two years all nine were razed to the ground.
The last to fall was Elgol flats in March 2000 in a televised explosion. "The final reminder of Manchester City Council's presence on the Darnhill estate disappeared with a big bang on Sunday," the Heywood Advertiser reported.
"High-rise Elgol flats turned into 6,000 tonne pile of rubble within seconds when 30kgs of explosives were placed around its 13 floors and exploded."
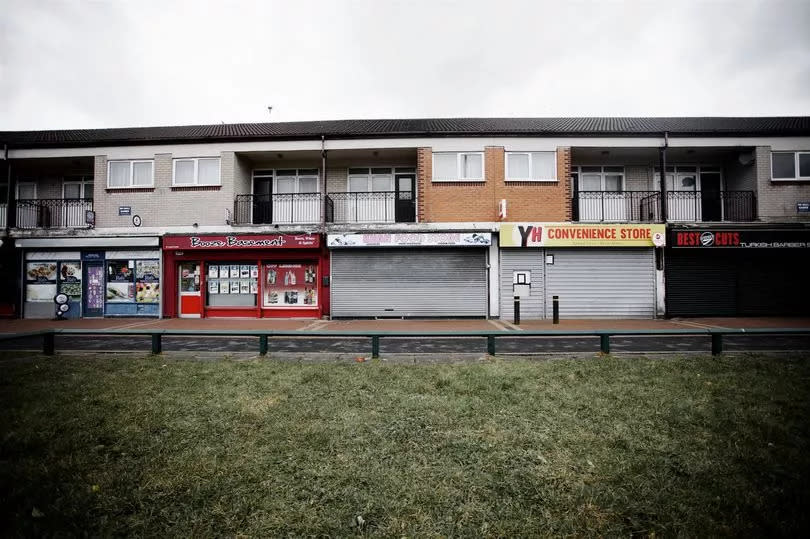

But while the demolition of the flats might have severed Manchester council's links to Darnhill, the estate still retains its Mancunian connection. To this day it's said people from Darnhill have a different accent to the rest of Heywood, with traces of the Manc twang clearly audible.
"Whenever I go back to Heywood I get the 163 bus, just because I feel at home," said Maria. "All the people who get on have that Darnhill accent, it's passed down through the generations.
"I think the Manchester connection will always be there and there's still a community on Darnhill, like there always has been."

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
