How Iran warned that Britain would pay for hosting dissident journalists

On March 29, Iran International television presenter Pouria Zeraati was walking the short distance between his front door and car in Wimbledon when a man approached him and asked for £3.
Suddenly, two other men surrounded him, putting him in a hold while their accomplice produced a knife. Zeraati, 36, was stabbed in the leg before the group ran away, travelling directly to Heathrow airport and fleeing the UK after leaving their victim bleeding on the pavement.
The 36-year-old survived the attack, which he sees as a warning – not just to him over his critical reporting of the Iranian regime, but to the hundreds of other Persian-language journalists who have become the target of attempted assassinations, stalking, harassment, threats and intimidation by Iran, its proxies and supporters.
By last February, police and the security services had responded to 15 credible Iranian threats to kill or kidnap UK-based individuals in little over a year, and similar plots have been uncovered worldwide.
Journalists suspect that many more incidents have links to Iran that were never proved, with harrowing testimonies given to a new report by press freedom group Reporters Without Borders including a 2005 incident in which a female reporter found a man waiting inside her home.
“I started screaming. I shut the door and I started running down the stairs, but he ran and he grabbed me,” the woman recounted. “I saw death.”
She was let go by the assailant, who stole her car and disappeared. A member of an eastern European criminal gang later confessed to the break-in, and although she believed Iranian authorities had ordered the attack a link could not be proved.
The report says that using hired criminals to do its bidding “is a known Iranian tactic, obfuscating the direct line to Tehran”.
But the Iranian government has made no secret of its attempts to sanction and shut down foreign-based news outlets, and in 2022 intelligence minister Ismail Khatib said Britain would “pay for its actions” by hosting them.
Iran International is now on “high alert”, says its spokesman Adam Baillie. “It’s what we’ve always dreaded and it’s happened. They didn’t kill Pouria, they slashed him – it was a very clear warning.”
Mehdi Hosseini Matin, the Iranian charge d’affaires in the UK, has denied any link to the stabbing, and while the Metropolitan Police said they are “keeping an open mind” on motivation, the force also noted: “Because the victim is a journalist at a Persian-language media organisation based in the UK, and previous threats had been directed towards this group of journalists, the incident is being investigated by specialist officers from the Met’s Counter Terrorism Command”.
It comes just months after the station resumed operations in London, having been forced to relocate on police advice because of plots against the lives of its journalists.
In December, a Chechen man was jailed for hostile reconnaissance at Iran International’s former premises at Chiswick Business Park, having been convicted for collecting information “likely to be useful for terrorism”. And in 2022, Iranian spies allegedly offered a people-smuggler $200,000 (£160,000) to assassinate two presenters outside the studio.
Reporters Without Borders (RSF) assesses that London has become a “particular hotspot” for the repression because of the high number of Iranian journalists working there.
The British capital is currently home to major broadcasters BBC Persian and Iran International, as well as several dissident Persian-language news websites, and until earlier this year also housed independent channel Manoto TV.
“Hundreds of Iranian journalists are based in London and that’s the reason we see a concentration of attacks here,” says RSF’s UK bureau director, Fiona O’Brien. “They are broadcasting in Persian and reaching a huge audience in Iran.”
Testimonies given by dozens of journalists detailed how they have suffered threats, abuse and intimidation for years, but that hostile activity by the Iranian government has spiked since 2022, when large anti-regime protests were sparked by the death of a 22-year-old woman arrested by the morality police.
O’Brien says that the repression and censorship of journalists inside Iran mean the regime fears external broadcasters “telling the story back to the Iranian people”, triggering a wave of legal sanctions against foreign-based outlets and renewed harassment of individual staff.
Targeted journalists also fear for their families, following the detention and interrogation of numerous relatives in Iran because of their loved ones’ work in the UK.
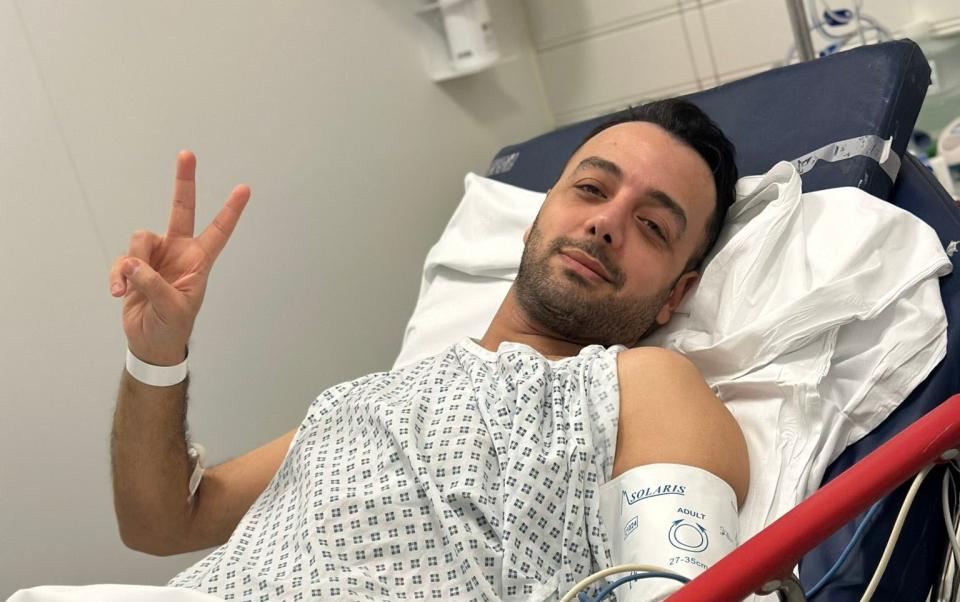
“There are times that I think I have a good story that I want to work on, but then I think is it really worth it?” one reporter said. “They are going to attack me, and maybe they are going to interrogate my mum again and she can’t tolerate it.”
Other journalists believe that their families are not even safe in the UK, with one reporter saying; “I wake up in the middle of the night. I check my son to see if he’s there. I don’t let him play in the garden on his own. I have to be there – I’m on alert constantly.”
The threat shows no sign of abating, with the BBC submitting a new complaint to the United Nations on Tuesday, reporting that several journalists had been convicted in absentia by a court in Tehran for “propaganda against the Islamic Republic”.
Senior Conservative MPs are calling for tougher action against the Iranian regime. The Government is facing pressure to proscribe Tehran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) as a terrorist group.
Sir John Whittingdale, who chairs the All-Party Parliamentary Group on Media Freedom, says that while counter-terror police had acted swiftly to protect Iran International, there was a “wider question about the government’s response to Iran”, adding: “The most recent incident takes it to a level which hasn’t happened before. The fact they felt able to carry out a physical attack on the streets of London is a clear escalation.”
The former culture secretary says that Iran cannot be allowed to act with “impunity” and is among those arguing for the IRGC to be banned, alongside fellow Tory MP Bob Blackman.
“Journalists are constantly under threat, when all they are doing is reporting in a free and fair way on what is going on in Iran,” he says. “I don’t think we’ve done enough to protect them. We’ve got to be much more vigilant and much more interventionist on our streets.”
Reporters Without Borders described the police response to complaints by Persian-language journalists as “mixed”, with some victims told to increase security precautions themselves or even advised to “turn it down a little” to attract less attention.
In some cases, local police officers deployed to investigate incidents were unaware of the context of complaints, leading them to dismiss cases too quickly. In others, they could not understand or translate threats made in Persian.
The testimonies come amid anger over the treatment of an Iranian dissident who has been arrested several times for lodging anti-Hamas protests at pro-Palestinian London marches.
The Metropolitan Police said Niyak Ghorbani had failed to comply with legal conditions imposed to keep opposing factions from clashing on several occasions.
This week, Ghorbani was detained in Westminster for holding a sign saying “Hamas is terrorist”, but the force later admitted he “should not have been arrested”. Former minister Robert Jenrick accusing the Met of “two-tier policing”.

Asked about the Met’s response to Iranian journalists, O’Brien said better training and guidance on Iran-related repression was needed, adding: “You have these horrific things happening and police are turning up at people’s houses with no idea what’s going on. I realise it’s very difficult with a force as large as the Met but there is more that could be done.”
Matt Jukes, the head of UK Counter Terrorism Policing, says officers are dealing with “growing demand” from Iran-linked plots, and are responding with protective security, plot disruption and personal safety advice, adding: “We know that some journalists who have chosen to make the UK their home are facing hostile intentions from foreign states. We are responding operationally and practically every day.”

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
