How to know if (and when) you’re going to go bald
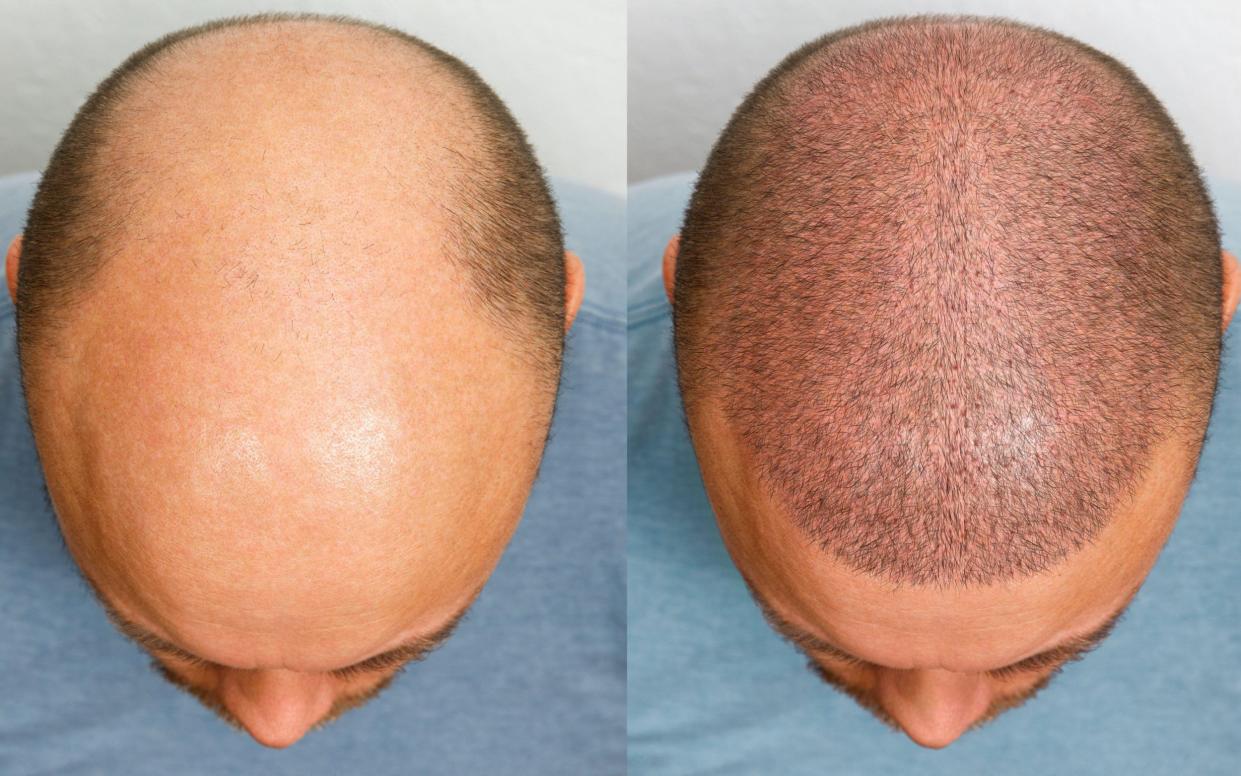
Losing hair is an issue many men worry about. That is understandable, because by the age of 70, between 96 and 100 per cent of men will have experienced noticeable hair loss. Around one in five start balding in their 20s, one in three in their 30s.
For those who look around at family gatherings and see the sun glinting off relations’ heads, that worry is doubled. But does a follicularly-challenged family automatically define your destiny?
“You can inherit the genetics for hair loss and that’s very often the case of both male and female pattern baldness,” says Eva Proudman, a fellow of The Institute of Trichologists, and a leading UK hair specialist. “It isn’t true that the gene for pattern baldness comes from your mum’s family. The gene can come through either side, mum or dad.”
There is a ray of hope for men intent on maintaining their locks in spite of bald family members. “The gene can skip generations and just because it runs in your family doesn’t mean you have inherited that gene,” explains Proudman. “If you inherit a dominant gene you will lose your hair. If you inherit the recessive gene, then you won’t. That’s why sometimes in a set of brothers, one will go bald and the other won’t.”
In fact, research has found 12 genes associated with baldness. “An important one is found within the X chromosome passed on down the female line, so if your mother’s father or brothers are bald, it is likely you’ll inherit that gene,” says Dr Marco Nicoloso, the medical director at hair loss clinic Ouronyx. “However, the other 11 are on non-sexual chromosomes and can come from either the father or the mother. So even if you inherit a genetic predisposition for male pattern baldness from your mother, all of your father’s genes could go in the opposite direction.”
How fast is male pattern baldness?
Of course, if they have many family members who’ve gone bald, leading them to believe they’ve inherited a “baldness gene”, some men will feel anxious about exactly when they might start to lose their hair. Unfortunately, there’s no easy answer.
“Half of men with androgenic alopecia [male pattern baldness] have experienced some hair loss by 35, but it’s very difficult to predict or estimate exactly when it’ll happen,” says Dr Nicoloso.
If a man has relatives who’ve lost their hair, they can provide a clue as to roughly when he might expect to start losing his.
“If your dad or granddad lost all their hair by 40, that’s likely to be when it happens for you too,” says Proudman. “However, it can happen later, because it depends on the other side of the family.”
Men will also inherit the pattern of their baldness, i.e. if your father started balding from the crown, you would too.
When is it typical to see first signs?
Given that it is based on a huge range of factors, hair loss can take place at different ages in different people. “I have men coming into my clinic at 14, but I also get men coming in at 70 who are experiencing hair loss for the first time, so it can happen at any age,” says Proudman. “As we age, all of us, men and women, experience hair thinning. It’s not the same as male or female pattern hair loss, but naturally the diameter and quantity of your hair thins a bit. It’s the same as getting wrinkles: a natural sign of the ageing process.”
But there are a lot of other elements involved in hair loss too. “Diet is a big factor in how fast it goes – being deficient in iron, vitamin D, zinc, and more generally protein, can all speed up hair loss,” says Dr Nicoloso. “However, it’s more common to see deficiencies in women. With men, the more common factors leading to faster hair loss are stress, smoking, drinking or excessive exercise.”
Male pattern baldness is caused by dihydrotestosterone (DHT) a sex hormone that plays a role in body, facial and pubic hair growth. High levels of DHT in the body can over-stimulate hair follicles causing them to miniaturise. This, in turn, causes the hairs they produce to become thinner, finer and lighter until eventually the follicle can no longer produce hair at all.
Excess testosterone production causes high levels of DHT. Studies have shown that certain types of exercises, such as resistance training and high-intensity interval training, can increase levels of testosterone, which explains why too much exercise can be a factor in hair loss. “Sometimes I’ll see guys at 18 who are starting to experience a bit of miniaturisation in their follicles, but it’s quite slow and you think they’ve got quite a few years before they’ll have any major hair loss, then they go to university and start bodybuilding, working out seven days a week, three hours a day, then they push up the amount of free testosterone in their bodies, that pushes up the levels of DHT which speeds up the balding,” explains Proudman.
How can you tell if you’re losing it?
If you’re anxious about losing your hair, especially when you have a lot of family members who’ve lost theirs, it’s easy to find yourself becoming paranoid every time a hair falls. But remember that hair loss is a slow process that takes months if not years to become obvious so there’s time to act.
The old adage is that once you start noticing you’re losing your hair, you’ve already lost a third, though Dr Nicoloso says that might be a bit drastic in 2024. “I think perhaps people are a bit more aware of it now, so they notice before they’ve lost that much,” he says, “but if you’re not wary, I’d say it’s certainly possible.”
Given 80 per cent of hair loss starts with temple recession, the best way to detect hair loss is to check your hairline. Measure from the glabella (the hard lump above the bridge of your nose, between the eyebrows), this is the one part of the face that doesn’t move or change with age. Measure from there to the centre of your hairline, and then 45 degrees to the left and right, to measure up to each temple.
Use these measurements as your baseline and repeat every few weeks. The wider and deeper the temple hair loss, the faster you’ll tend to lose your hair. If the measurements start getting bigger, that’s when to see a trichologist.
“The first thing to do is to have a consultation with a specialist and have a trichoscope [a microscope used for looking at hair follicles] analysis and to check the situation and to check what’s causing your hair loss,” says Dr Nicoloso. “From there you should look into treatment as soon as possible because all known options only work for existing hair follicles. Once the hair follicle is gone, there isn’t much we can do apart from hair transplants.”
One minor caveat is that “your hairline doesn’t mature until around about 25,” says Proudman. “Until then, you might feel like you’ve got temple recession or male pattern baldness, but it’s very likely to be your hairline just falling back to its natural shape. If there’s no sign of hair loss anywhere else on the head then you can be fairly sure it’s not male pattern hair loss.”
Bear in mind that stress can also cause hair loss, but that is different to pattern hair loss and your hair can come back.
What to do about hair loss
If you are losing your hair there are several treatment options that can help halt or even reverse the decline. As Dr Nicoloso notes though, all the treatments work on surviving follicles so it’s crucial to start early, before they can no longer produce hair at all.
“As long as you’ve still got a good amount of those miniaturised hairs, even if you can’t see them with the naked eye, then medications like minoxidil and finasteride can stabilise the hair loss and stop that miniaturisation being so aggressive,” explains Proudman.
You can read the Telegraph guide to finasteride and minoxidil here, but in brief, both prevent the conversion of testosterone to DHT, stopping the miniaturisation of hair follicles. It’s worth noting, however that there has been some criticism of finasteride, with some men reporting side-effects including depression and sexual dysfunction. Studies have been inconclusive on the degree to which side-effects are psychosomatic, with around 3 per cent of men experiencing them.
Be warned though, that while these treatments are largely effective “some people respond better than others,” adds Proudman. “In some people they can fully halt the hair loss, whereas others will just be slowing down the process. Then there are some who stop losing hair at first, but as they get older the medications don’t work as well and it starts up again. In that case, you’re looking at a hair transplant.”
There are also a couple of more recently developed options that are less invasive than a transplant. “Micrografting, also known as Autologous Micrografting Technology (AMT) takes cells from behind your ears where the donor follicles are strongest, then those are processed to create cells that encourage hair growth,” explains Dr Nicoloso whose clinic specialises in this treatment. “Those are injected all over the head and can stimulate damaged hair follicles and restore their functionality.”
The other new treatment uses a handheld device called a trichopat which uses micro skin incisions and acoustic sound waves to increase blood flow to the scalp and reactivate cellular metabolism of hair follicles, boosting their ability to grow hair.
Ultimately, it’s important to remember that regardless of your dad, grandfather or uncle’s head of hair, yours isn’t necessarily doomed, as long as you’re prepared to work at keeping them in tact.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
