Scientists to release irradiated mosquitoes to fight dengue fever
Mosquitoes zapped with radiation to make them sterile are set to be released into the wild in a bid to fight outbreaks of dengue fever.
The World Health Organization has announced that from next year it will start large-scale studies of what is known as the sterile insect technique. This involves irradiating male Aedes mosquitoes, the species responsible for the spread of diseases such as dengue, Zika and chikungunya.
The scientists hope that the sterile males will be released in such large numbers that they will overwhelm the native male population and then go on to mate with females.
But they will produce no offspring so the insect population will reduce over time, alongside the number of cases of the disease.
The technique has been used for about 50 years in the management of agricultural pests, such as the Mediterranean fruit fly, and experts are confident that it poses no risk to either human health or the environment.

WHO has been working with organisations including the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and the Food and Agriculture Organisation on preliminary studies in countries including Bangladesh, Cuba, Brazil and Mauritius.
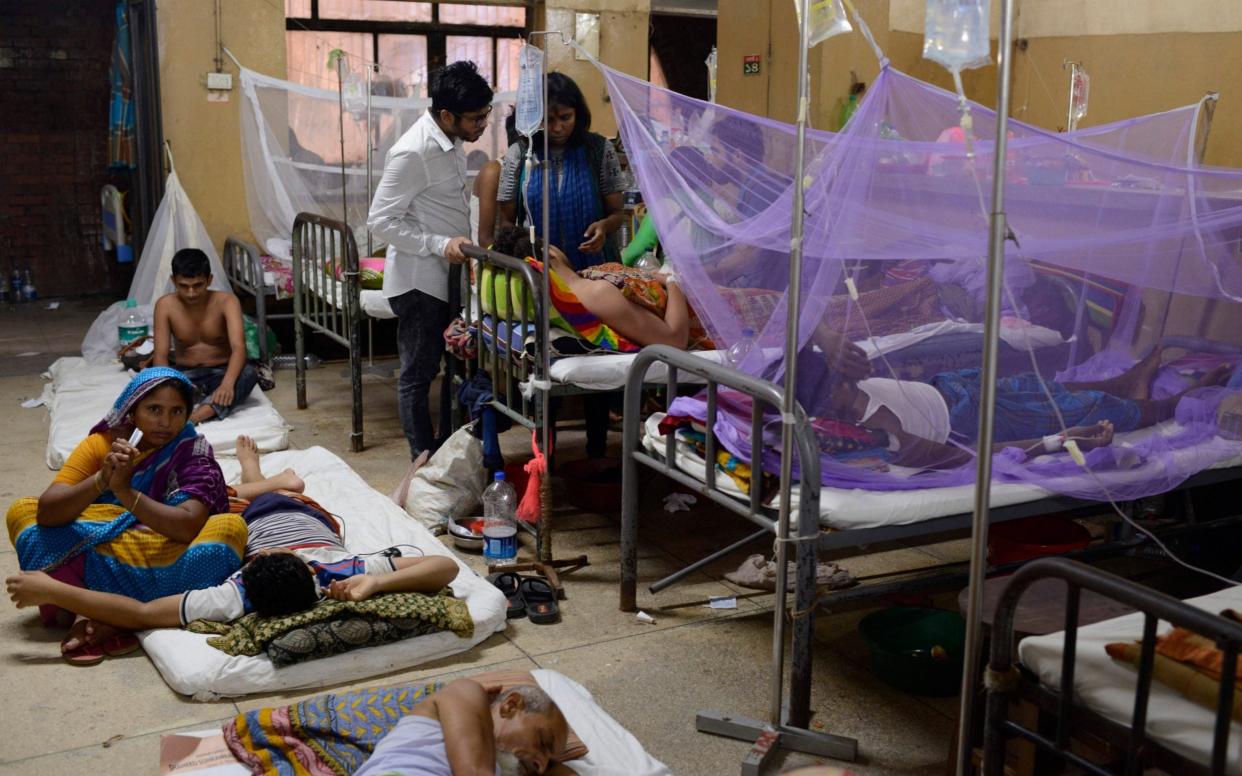
Dengue fever has become a major health threat with 110 countries around the world suffering outbreaks this year. WHO believes that as many as five million cases may be reported by the end of 2019 - up from an average of three million in previous years.
Urbanisation and climate change are expected to see the mosquito responsible for transmitting the disease spread to new areas.
Raman Velayudhan, coordinator of WHO’s department of neglected tropical diseases, said there was a desperate need for new tools to control the Aedes mosquito which lives in urban areas, bites during the day and whose eggs are able to survive for long periods.

“It’s a unique mosquito which has silently expanded and today is present in over 130 countries,” he told a press conference, where the trial was announced.
Experts insist the technique is safe - the mosquitoes are not “radioactive” and there is no genetic mutation.
WHO also stresses that the technique will not harm the wider eco-system. There are more than 3,500 different types of mosquito that serve as food for animals so removing one species will have little impact.
The IAEA is looking at refining the technique for malaria-carrying mosquitoes, although Dr Velayudhan said there were already control tools for this mosquito, such as bed nets and indoor residual spraying.

Florence Fouque, a tropical disease expert at WHO, said the technique could have a “really significant” impact on dengue.
“We have to demonstrate that this technology has an impact not only on the density of mosquitoes but on the number of cases of the disease: declining, reducing and eventually eradicating a disease in a country,” she said.
Dr Velayudhan added WHO hopes to reduce the mosquito population in trial areas by a quarter by 2025 and 2030.
Dr Soumya Swaminathan, WHO chief scientist, added: “Despite our best efforts, current efforts to control [dengue] are falling short. We desperately need new approaches and this initiative is both promising and exciting.”
Protect yourself and your family by learning more about Global Health Security

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
