'We don’t want chaos and confusion': Meet the woman behind the new GCSE grades
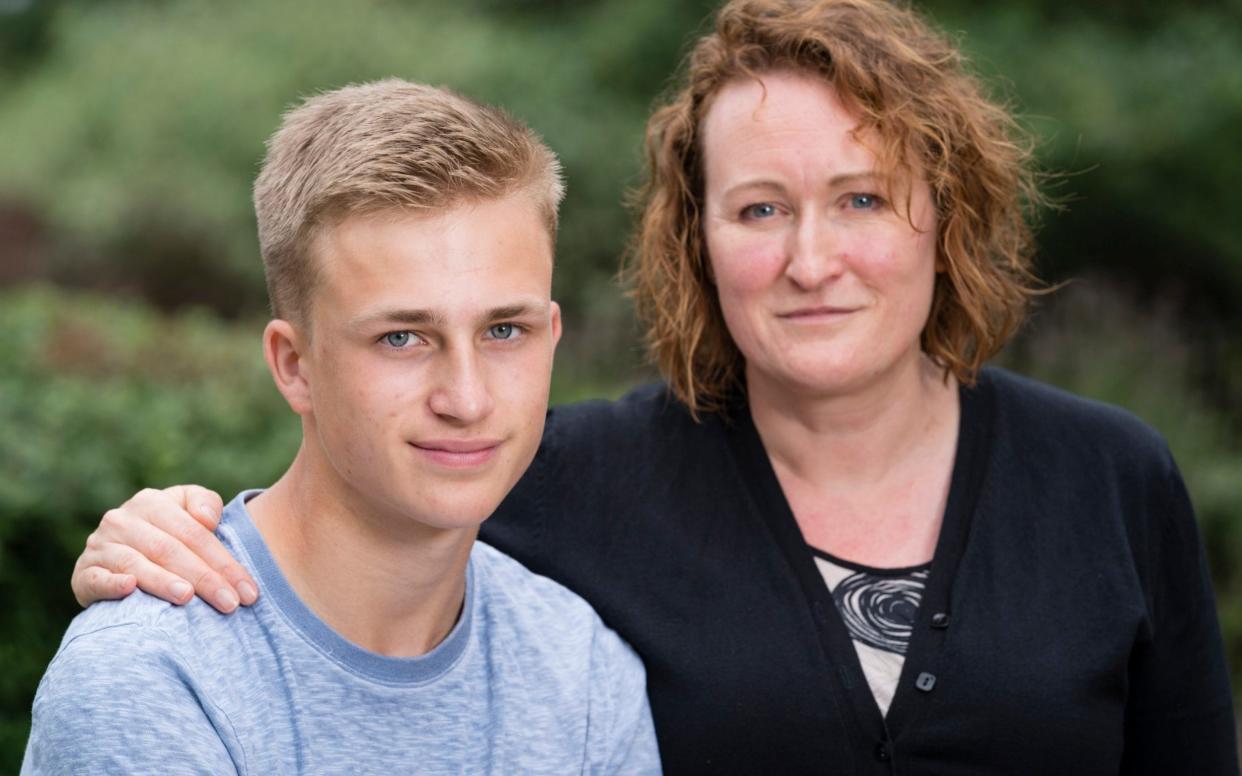

For thousands of parents up and down the country, three weeks today will bring a feeling of apprehension, as GCSE results day rolls around. In Cath Jadhav’s case, though, the hope that everything runs smoothly will be especially acute.
As well as being the mother of 16-year-old Luke, one of those pupils nervously awaiting August 24, Jadhav is the Associate Director of Standards and Comparability at Ofqual - the Government department that regulates qualifications in England. Effectively, it is her job to ensure the entire GCSE programme is successful. And this year, she has overseen its biggest upheaval in decades.
Instead of the A* to G grades by which GCSE pupils have been assessed since the mid-Nineties, candidates who took English language, literature and maths exams in 2017 will be marked under a numerical system that ranges from 9-1. Another 10 or so subjects will follow suit next year, before the whole curriculum is on board by 2019.

Sitting alongside Luke in Ofqual’s headquarters in Coventry, Jadhav, 48, warmly explains the point of all this. The idea, she says, is that by dividing grades up even more it will be easier for teachers, colleges and potential employers to differentiate between average students and excellent ones.
“At the moment, around 60% of GCSE results are Bs or Cs, and when we spoke to employers and people in higher education, they said they wanted a way of knowing the difference between everyone.
“To do that you need an entirely new grading scale. If we’d just made a B in 2016 easier to get than a B in 2017, that would have been confusing. Employers are already cottoning on well, and so are schools, we think.”
The new system contains deliberate “anchor points” by which conversion to the old grades is possible.
Ofqual is at pains to emphasise against direct comparisons but, roughly speaking, an old A is a new 7, an old C is a 4, and an old G (not that you’d ever wish to acquaint yourself with a G) is a 1. The idea, they say, is that the same proportion of students will get a 4 and above as currently achieve a C grade or higher, and broadly the same proportion of students will get a 7 as are currently graded A. It means there will be a greater spread, but fewer top grades. So a set of ‘straight 9s’ will be harder to achieve than an old set of straight As.
“We hope that’s taken into account before results day. In English and Maths this year there simply won’t be as many 9s as there used to be A*s. I think we’ll see fairly stable results, but we don’t want chaos and confusion on the day.”
Jadhav has worked with Ofqual for eight years, and likens changing educational qualifications to “turning one of those giant oil tankers around.” The new grades have been in the works for around four years, and are a by-product of a comprehensive Government white paper presented to Ofqual during Michael Gove’s tenure at the Department of Education.

That report also suggested an end to ‘controlled assessment’ – better known as coursework – and modules in favour of a linear GCSE curriculum, with all assessment at the end of the two years.
Luke, who goes to school near the family home in Kenilworth, has been one of the first pupils to experience the Goveian vision, and thinks having no coursework is a good idea
“Coursework can be sort of unfair, sometimes, because teachers can find gaps in the rules to help people,” he says. “I think it’s better to not have it and save everything for the end.”
“There are suspicions that some schools have perhaps been providing a bit more help for some students than others, for whatever reason, during coursework, so this levels the playing field,” chips in Jadhav. “Subjects like Art and PE obviously can’t be assessed at once, but where possible, it will be all be exams.”
Luke is the eldest of her two sons (the younger is in year 8), so Jadhav has the unique experience of overseeing a set of exams that her own children will take part in. Still, that doesn’t make her a tiger mother. “At parents evening I try and be ‘Mum’ and not from Ofqual,” she says.

There are plenty of parents of teenagers working at Ofqual, Jadhav adds, and she is keen that the organisation isn’t seen as a bunch of “faceless bureaucrats” – shaking things up without consideration for the pupils.
“People sometimes forget we in the industry have kids, too, and think we just change things for the sake of it. But we’re always trying to communicate the fact we work for years to make change as easy as possible,” she says.
It’s certainly not the easiest job. So where will the family, including Jadhav’s partner Mark, a part-time professional football referee, be three weeks today, as results – and Ofqual – hit the headlines?
“Oh, we'll all be here,” she says, with a laugh. “But after that we’re going to West Wales, where there will be no WiFi and no e-mail. It will be good to go off-grid, I think.”

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
