BAE to work on the first new supersonic fighter jet in almost 40 years
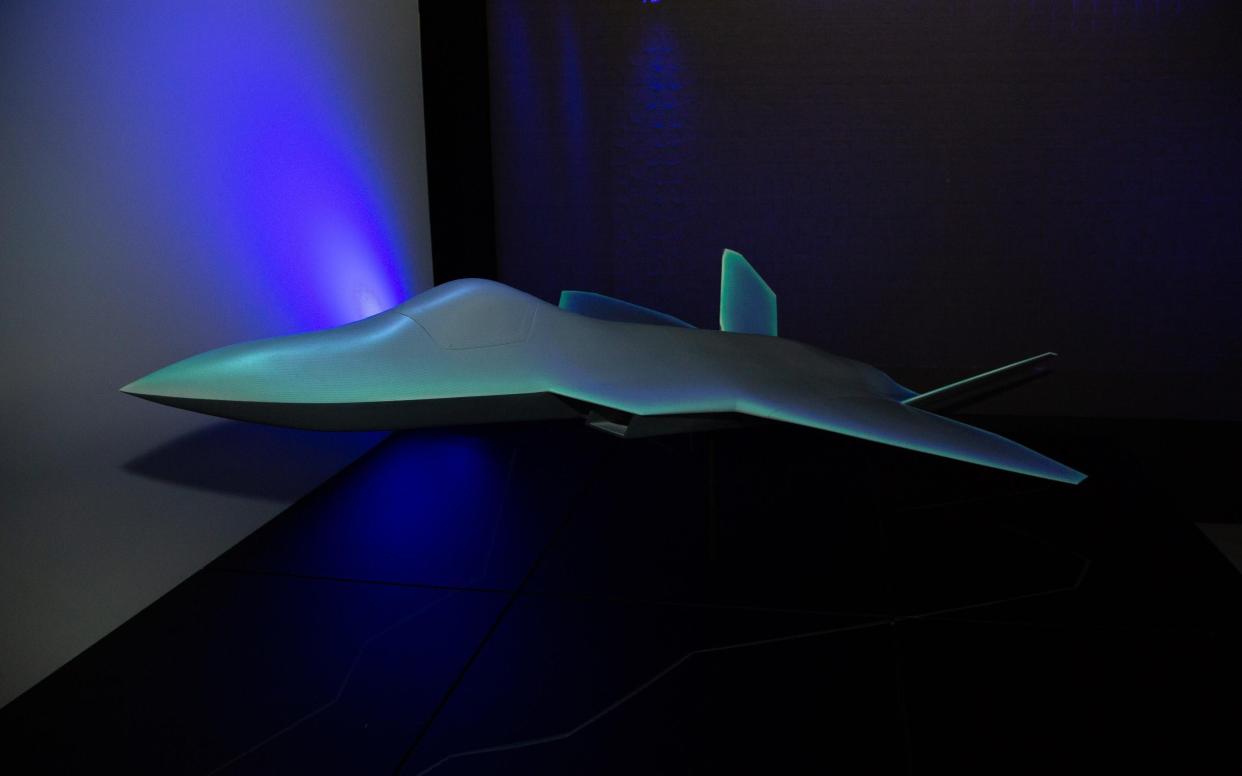
BAE Systems is to begin work on its first supersonic fighter jet prototype in almost 40 years as part of its Tempest programme.
The defence giant will develop a sixth-generation warplane to replace the Eurofighter Typhoon. The flying prototype will be a venture between BAE and the Ministry of Defence – a distinct project within the wider Tempest programme, which also involves Italy's Leonardo.
Separately, the Government announced on Monday that the UK is conducting “joint concept analysis” with Japan. That could see the nation eventually join the Tempest fighter jet programme. Japan offers both considerable technology experience and financial weight.
Developing a prototype is seen as a key step in testing the planned design of the new fighter jet. BAE's predecessor, British Aerospace, made a demonstrator in 1986, which was ultimately developed into the Typhoon. That was the last time the UK built a supersonic fighter prototype.
Herman Claesen, managing director of future combat air systems at BAE, said the new prototype could propel the company’s technology forward in similar-sized leaps to the development of the jet engine or the Concorde passenger jet.
He told journalists at the Farnborough airshow: “This is in the same category as when Sir Frank Whittle developed the jet engine, when we designed Concorde, this is a fundamental step forward from an engineering point of view in doing combat.”
BAE wants the new fighter jet to be flying “in the next five years”, according to Mr Claesen, who added that about 1,000 people will work on the design of the demonstrator at BAE and its suppliers.
The jet will be a so-called sixth-generation fighter, which offers better radar-beating technology than the fourth-generation Typhoon and fifth-generation carrier-based F35, which was a project led by US firm Lockheed Martin on which BAE had some work.
The prototype will be fitted with jet engines developed by Rolls-Royce. Rolls signed a deal last year with Japan’s IHI to develop a next-generation engine, which added to speculation that Japan could join the programme as a full member.

In common with the F-35, the fighter will be loaded with sensors and high-power computer systems designed to gather and process data and turn it into intelligence on the battlefield.
The newest systems require vast amounts of electric power and Rolls and BAE will need to work out how to deliver it whilst also keeping the plane away from detection.
The company has registered more than 50 patents and worked with 100 suppliers, small business and universities to do the research so far, said Mr Claesen.
Much has changed since the last prototype was made in the 1980s, Charles Woodburn, BAE Systems chief executive, said. Paper drawings have given way to three-dimensional digital models, which can be tested in computer simulations before they are made.
“There has been a lot more design work done digitally now compared to back then. So we have a much clearer picture of what it will look like, how it will fly,” he said.
Farnborough Airshow is typically used by the defence and civil aviation industries as a venue for announcing big deals.
Sources say that an announcement about Japan joining the Tempest programme is unlikely this week and that Tokyo will make a final decision on the direction of its own new fighter programme later this year.
Reuters reported last week that Tempest and Japan’s F-X programmes could be merged. This would create an Anglo-Japanese-Italian powerhouse which would compete for international business with France and Germany’s own future combat jet project.
Defence Secretary Ben Wallace said: “I am delighted that the UK, alongside Italy and Japan, are working on similar combat air journeys together. Our work with Japan and Italy on cutting-edge technology like this shows the benefit of our alliances across the world.
“The design and development of the demonstrator aircraft represents an important milestone, showcasing the success and talent of our engineers, programmers and software developers. This programme will go on to attract opportunities for many more great minds and talent from across the UK.”

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
