Brits warned of rise in ticks carrying potentially fatal diseases due to climate change
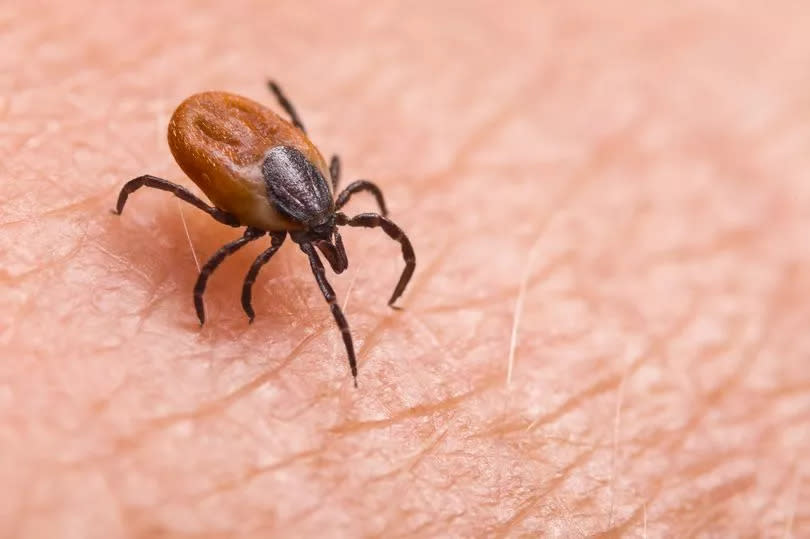
Brits are being warned of the increasing danger of tick bites in the UK as they can carry potentially fatal diseases.
Climate change bringing a warmer and humid climate to the country means that there are likely to be more ticks which in turn could increase the number of cases of Lyme disease, according to the UK Health Security Agency.
And another tick-borne disease that could see an increase in cases is babesiosis, caused by the babesia parasite, and which infects red blood cells. It symptoms are similar to Lyme disease but babesiosis more often starts with a high fever and chills and as the infection progresses, patients may develop fatigue, headache, drenching sweats, muscle aches, chest pain, hip pain and shortness of breath.
Lee Mack stunned as quarter of 1% club contestants wiped out by early question
Get all the latest TV and showbiz news and gossip from Chronicle Live with our free newsletter
"Babesiosis is often so mild it is not noticed but can be life-threatening to people with no spleen, the elderly, and people with weak immune systems," states lymedisease.org. "Complications include very low blood pressure, liver problems, severe hemolytic anemia (a breakdown of red blood cells), and kidney failure."
There has been an increase in people reporting tick-borne conditions like Lyme disease and babesioisis. The UKHSA states: "Ticks can be active all year round, but they are most active in the months April to July, and sometimes later in the autumn. Activity continues over the winter months but at a significantly reduced level. So, we are reminding people to be 'tick aware' as they enjoy the great outdoors at any time of the year."
The UKHSA has also said that warmer conditions mean that there are more "favourable conditions" for ticks and it will lengthen the period of time when they are active. Jolyon Medlock, head of medical entomology at the UKHSA, said that ticks from other parts of Europe will spread to the UK.
He told Sky: "As climate warms in the UK in the coming decades, species that are not normally found in the UK might suddenly appear. If there are more people exposed to ticks, we are likely to see more cases of Lyme disease in the future."
Studies in Europe estimate that 1% to 5% of tick bites can lead to Lyme disease. On average, approximately 4% of ticks are infected in England and Wales, although this range can fluctuate in different areas and across years, and can be on average as high as 8-10% in some areas.
Where are ticks found?
Ticks are common in grassy and wooded areas and those involved in hiking, cycling or camping, should be more wary of them, but they can also be found in urban gardens.
How to avoid infections
To avoid tick-borne infections people should wear clothes which cover skin to make it more tricky for the bugs to find a suitable place to bite. They should use repellents such as DEET and wear light-coloured clothing to easily spot ticks and brush them away. They should also check their clothing, pets and others they have been with for ticks. If any are found they should be removed with a tick-removal tool or fine-tipped tweezers.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 
