Futuristic device is helping scientists break solar-efficiency record
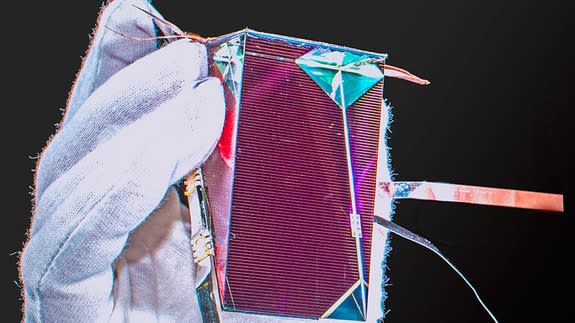
Looking a little like the world-saving stones from sci-fi classic The Fifth Element, a new device is expected to have a big impact on renewable energy.
Built by Mark Keevers and Martin Green from the University of New South Wales (UNSW), the unique prism could help make solar panels cheaper and more efficient. In fact, it's already broken a world record for the amount of solar energy it can create from unfocused sunlight.
SEE ALSO: The challenges of building a global startup in six new languages
The prism has a sunlight-to-electricity conversion efficiency rate of 34.5 percent, Keevers told Mashable Australia. That's about a 44 percent improvement in efficiency on the previous record, he said, which sat at 24 percent efficiency but over 800 square centimetres (124 square inches). The UNSW team's record was achieved over a smaller surface area of 28 square centimetres (4.34 square inches).
Importantly, it does this with normal, un-concentrated light — the type household solar panels already use.
The number has been independently confirmed by the U.S. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (USNREL), Keevers added. The USNREL has been contacted for comment.

Image: UNSW
The device works by splitting sunlight into four bands. Inside the prism, solar cells use a particular type of semi-conductor material, such as silicon, to optimally convert a particular band of sunlight into electricity.
The prism also uses high-purity glass and a special filter to help steer the sunlight so it stays mostly trapped inside, eliminating wastage.
Despite the excitement, we're still a long way off seeing one of these prisms on every rooftop. "Right now, this is a proof of concept prototype," Keevers said. "Of course, it's expensive and we've used expensive materials and techniques." The mini-module cost roughly $3,000 to create, which he said was normal for a lab experiment.
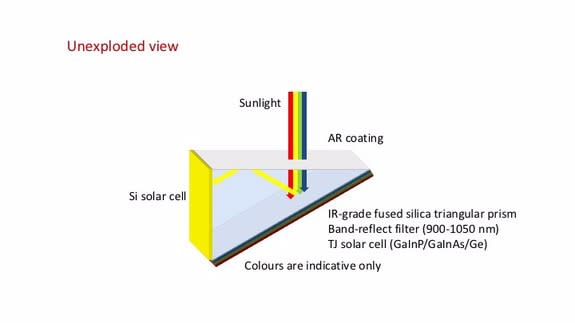
Image: UNSW
Once costs are reduced, such prisms could be installed on a larger scale for rooftop use. "Instead of what you can get now, which is typically, say, 17 percent [efficiency] modules for your rooftops, in 10 or 20 years, you might be able to buy 34 percent efficient modules, so you'd need half as many for a rooftop to get the same electricity out."
Importantly, with this invention, the solar industry may be able to increase efficiency much sooner than expected. "We're not going to be there tomorrow, but maybe in 10 or so years time, we could be at 34 percent for commercial modules ... it's a possible path to getting higher efficiency sooner," he explained.
Next on the agenda, the team will be pursuing still higher rates of efficiency, but also lower costs. "Efficiency and cost — they're everything that matters," Keevers said.

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 