Poorer people in Kensington will ‘live for 16 years less than their richer neighbours’

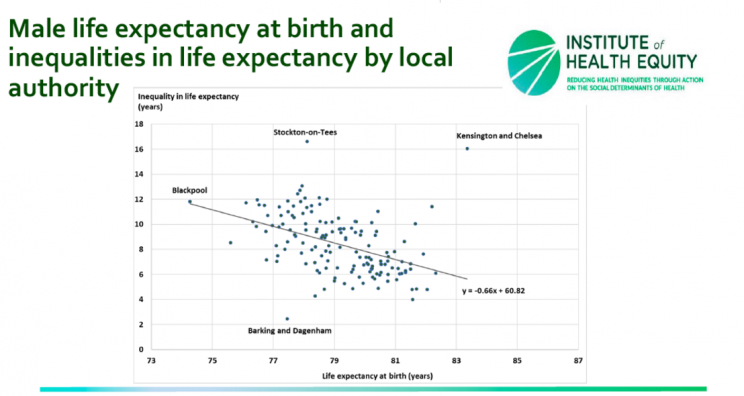
People in rich areas of Kensington and Chelsea can expect to live for 16 more years than their poorer neighbours in the same council area, a study says.
The shocking statistic reveals that those in poorer parts of the London borough, like the area that includes the Grenfell Tower, will not live as long as their more affluent counterparts.
Men in Kensington and Chelsea will live for 16 fewer years if they are in a poorer area, according to a life expectancy report by the Institute of Health Equity at University College London.
Its author, Sir Michael Marmot, warned that rises in life expectancy across England have almost ‘ground to a halt’ as a result of austerity.
He said he was ‘deeply concerned’ that increases in life expectancy had levelled off since 2010 and that it was ‘entirely possible’ that austerity – including a wave of Conservative Party cuts – is having an effect.
He said the stagnation needs “urgent” investigation.
Historically, improvements in life expectancy at birth had been around a one year increase every five years for women and every three and a half years for men.
But since 2010 this has slowed to a one year increase every 10 years for women and every six years for men, new analysis has shown.
MORE: Grenfell Tower: Less than 6 per cent of donated goods given to survivors
MORE: Woman wearing short skirt in public causes uproar in Saudi Arabia
Expected rises in life expectancy when people are aged 65 have also slowed.
Sir Michael, who previously chaired a government-commissioned review into health inequalities, said the rate of increases ‘is pretty close to having ground to a halt’.
He added: ‘I am deeply concerned with the levelling off, I expected it to just keep getting better.
‘I would say it is a matter of urgency to try and examine why this has happened – it is not inevitable that it should have levelled off.’
He said he could not draw conclusions as to why rises in life expectancy have faltered.
But he raised concerns about ‘miserly’ health and social care spending.
‘I am deeply concerned that if we do not fund health care and social care adequately people will lead much worse lives,” he said.

He said that spending on ‘social expenditure is among the most miserly of Western European countries and our spending on health care is miserly’, adding: ‘Because we are blessed with the National Health Service, the Commonwealth Fund continues to give high ratings.
‘We need to preserve this valuable national recourse but that means we have to spend appropriately because the need is going up because of the rise in older people.
‘If we don’t spend appropriately on social care, if we don’t spend appropriately on health care, then certainly the quality of life will get worse for older people and maybe the length of life too.’
Sir Michael, who is director of the Institute of Health Equity, said there are now many more older people, adding: ‘We’ve got many more older people at very old ages and life expectancy is stagnating so problems that affect older people are going to be more numerous.’
He also highlighted that the leading cause of death among the oldest old is now dementia and Alzheimer’s.
‘Dementia on the death certificate is the tip of the iceberg. If people are dying of dementia that means there is a lot of people living with dementia.’
From 1978/79 NHS spend in real terms increased about 3.8% per year but from 2010 it increased at about 1.1% a year, ‘significantly below the long term trend’, he said.
Meanwhile, between 2009/10 and 2015/16 the spend on adult social care went down by 6.4%, he added.
‘Our spend on healthcare is going down, our spend on adult social care is going down and all the indicators suggest that the need is going up. It is not a good combination.
‘The cuts in social spending, the failure of the NHS to continue to rise in spending per person is having a significant impact on social care for the very old.
‘We see the rise in dementia which is very troubling and that will require an increase in health and care spending and that’s not happening.’

Commenting on the analysis, Jeremy Hughes, chief executive of the Alzheimer’s Society, said: ‘Every day through our helpline we hear how the chronic lack of funding to the social care system over the last decade is devastating people with dementia.
‘This latest analysis suggests just how far-reaching the consequences of austerity have been for the most vulnerable in our society.
‘The government has to act before the care system collapses entirely. The promised consultation on social care reform can’t be a platitude or a way to buy more time. We need a long-term solution for social care, and – crucially – enough funding to implement it.’
A Department of Health spokesman said: ‘Just last week, the NHS was rated the number one health service in the world. Life expectancy continues to increase, with cancer survival rates at a record high whilst smoking rates are at an all-time low.
‘We continue to invest to ensure our ageing population is well cared for, with £6bn extra going into the NHS over the last two years and an additional £2bn for the social care system.’
(Main picture: PA)

 Yahoo News
Yahoo News 

